Manufacturers need visibility to connect their products and services with the local market, while ensuring that the general public values what manufacturing does for the city.…
Read more
Providing transparency in environmental, economic, and social processes helps building trust and acceptance of urban manufacturing, while also founding a basis for interaction and collaboration between businesses.…
Read more
The curator helps businesses or neighbourhoods by aligning interests, building partnerships, exploring needs, communicating news and protecting community interests.
Read more

A diversity in job opportunities that are fairly distributed across the city allows for workplaces to fit the skills, capacities and interests of the local workforce, provides businesses with options for staffing while ensures cities are resilient and accessible.…
Read more

Fair working conditions are integral for providing good quality output, a reliable and agile workforce, a strong brand and in turn to promote manufacturing businesses as a valuable source of employment.…
Read more
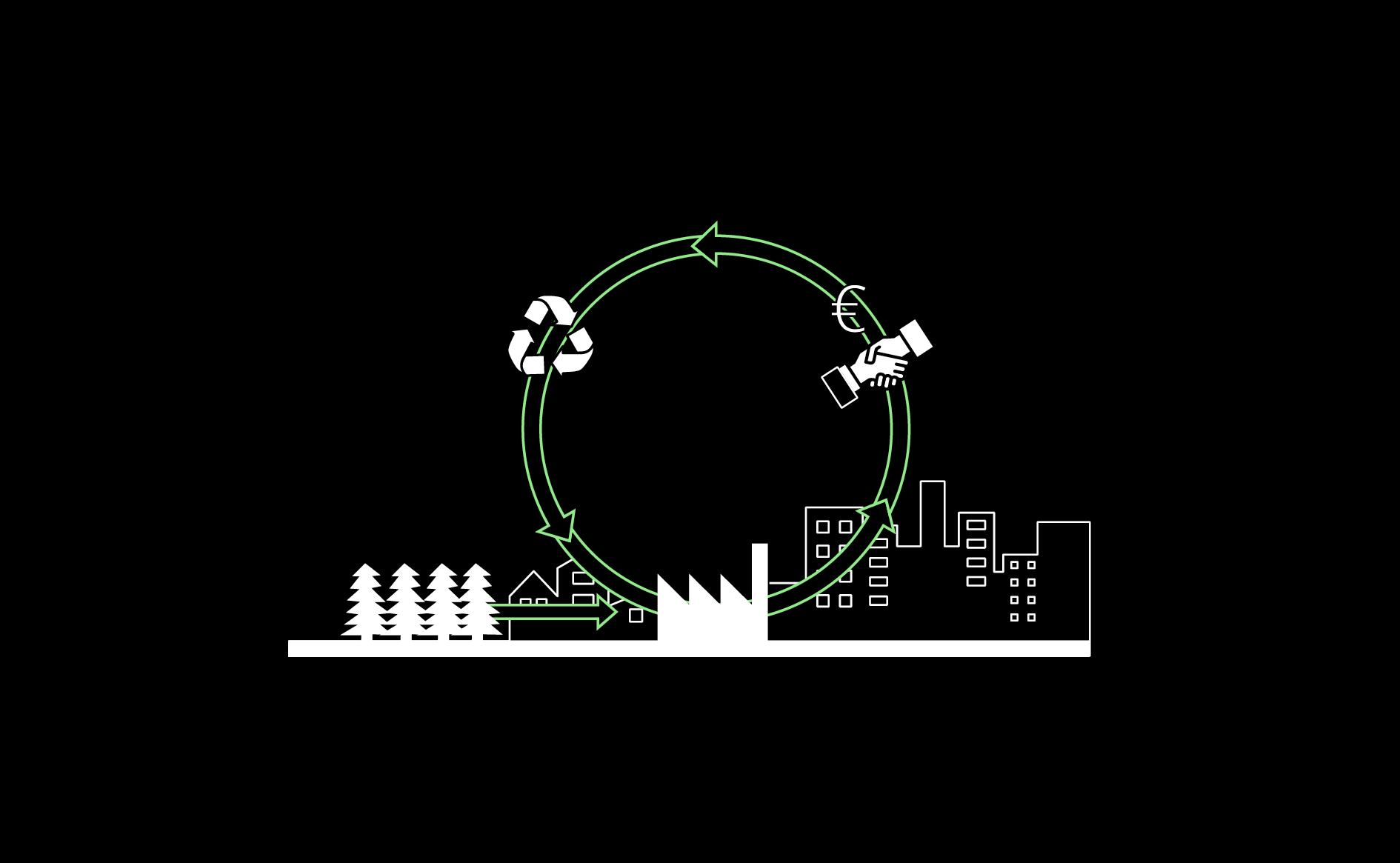
Manufacturing contributes to city-scale circularity, helping reduce distances from resource to processing site, distribution and retail, and then to re-use, remanufacture, material recovery and back to the production cycle.…
Read more
A system of integrated infrastructure at different scales is required to manage resource flows (materials and energy) and to promote effective circular economy approaches. …
Read more
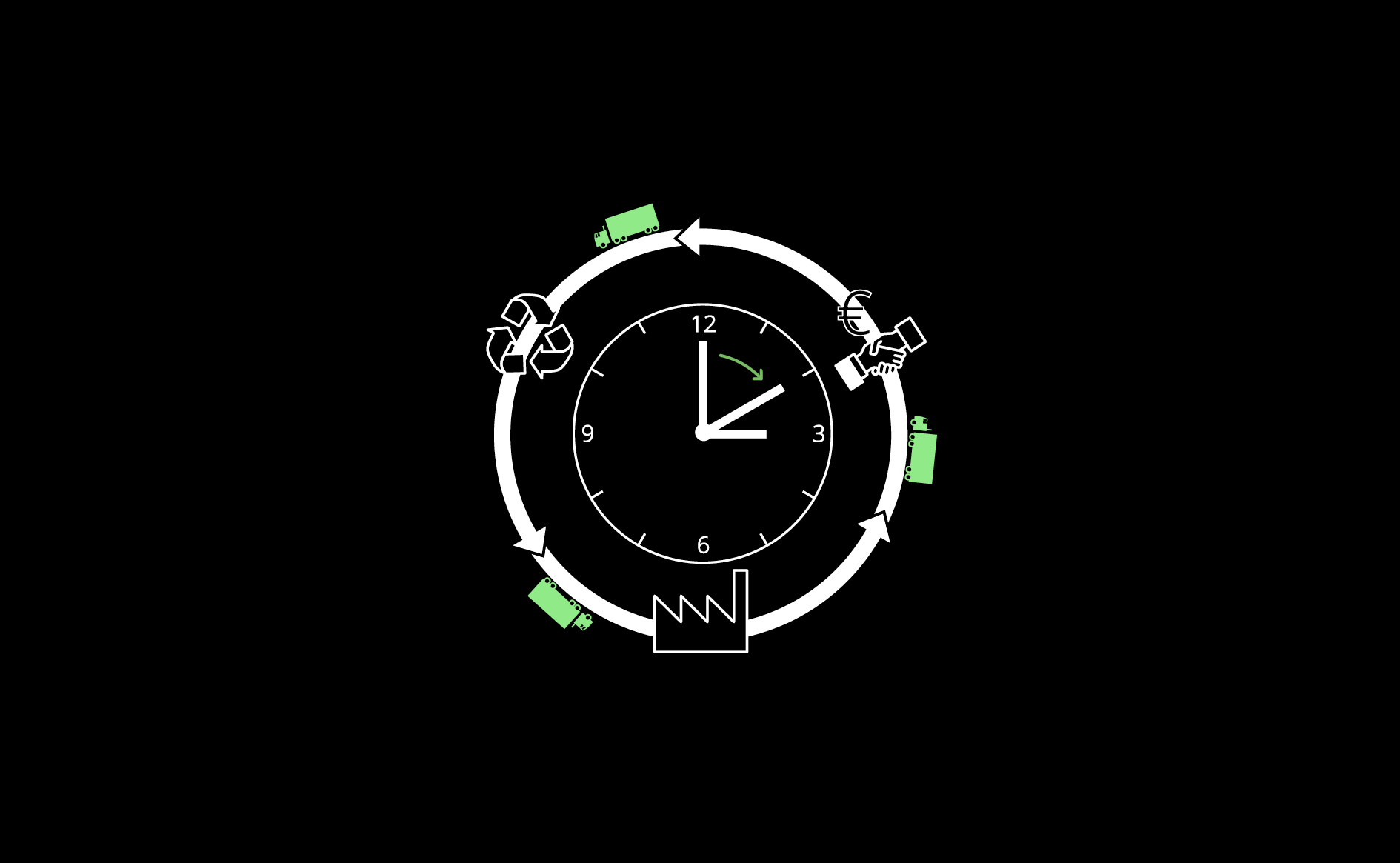
Time-distance efficiency in logistics contributes to sustainable and competitive manufacturing.
Read more
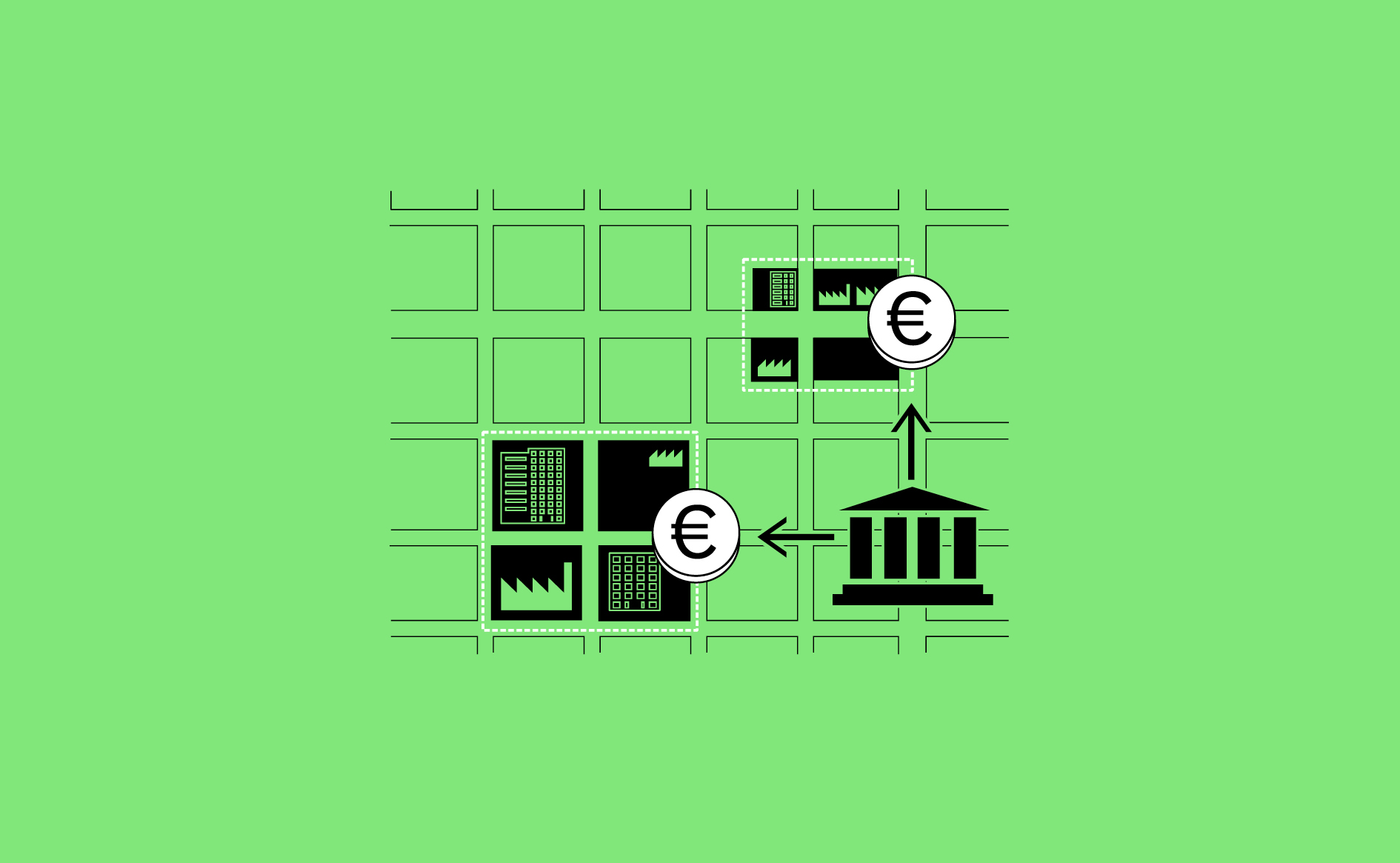
Businesses require reliable long term access to their manufacturing space in order to make investment in staff, technology and local networks.…
Read more

Financial instruments are important mechanisms to improve neighbourhood scale infrastructure and technology, while rendering businesses more compatible with their context.
Read more
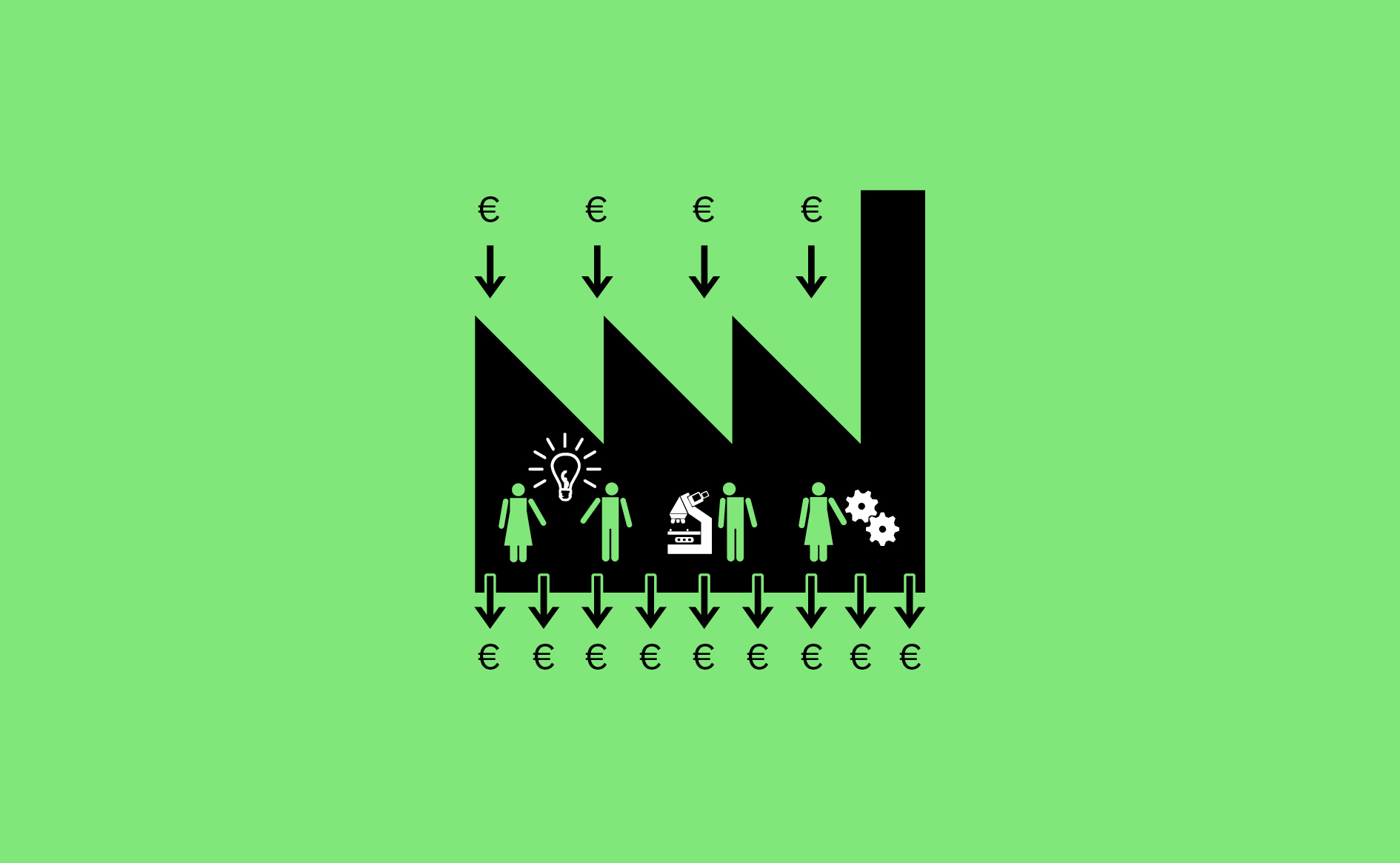

Cities can stimulate research and development through incentives such as providing finance and space, offering technical support, business development and support with tenders.…
Read more
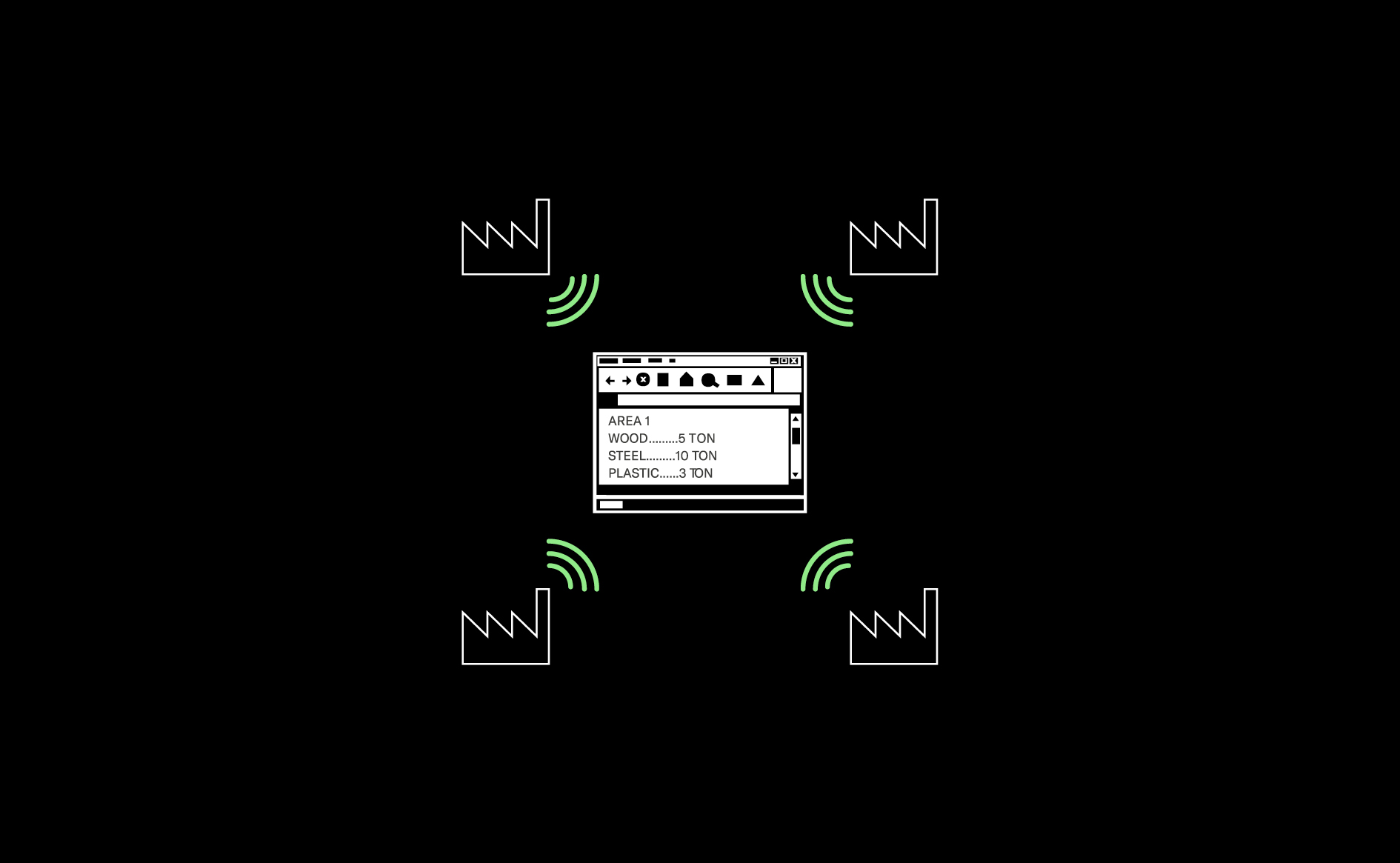

A centralised spatially connected database, containing data on flows of material (and waste), helps to facilitate and optimise local distribution of resources and maximise opportunities for material recovery.…
Read more
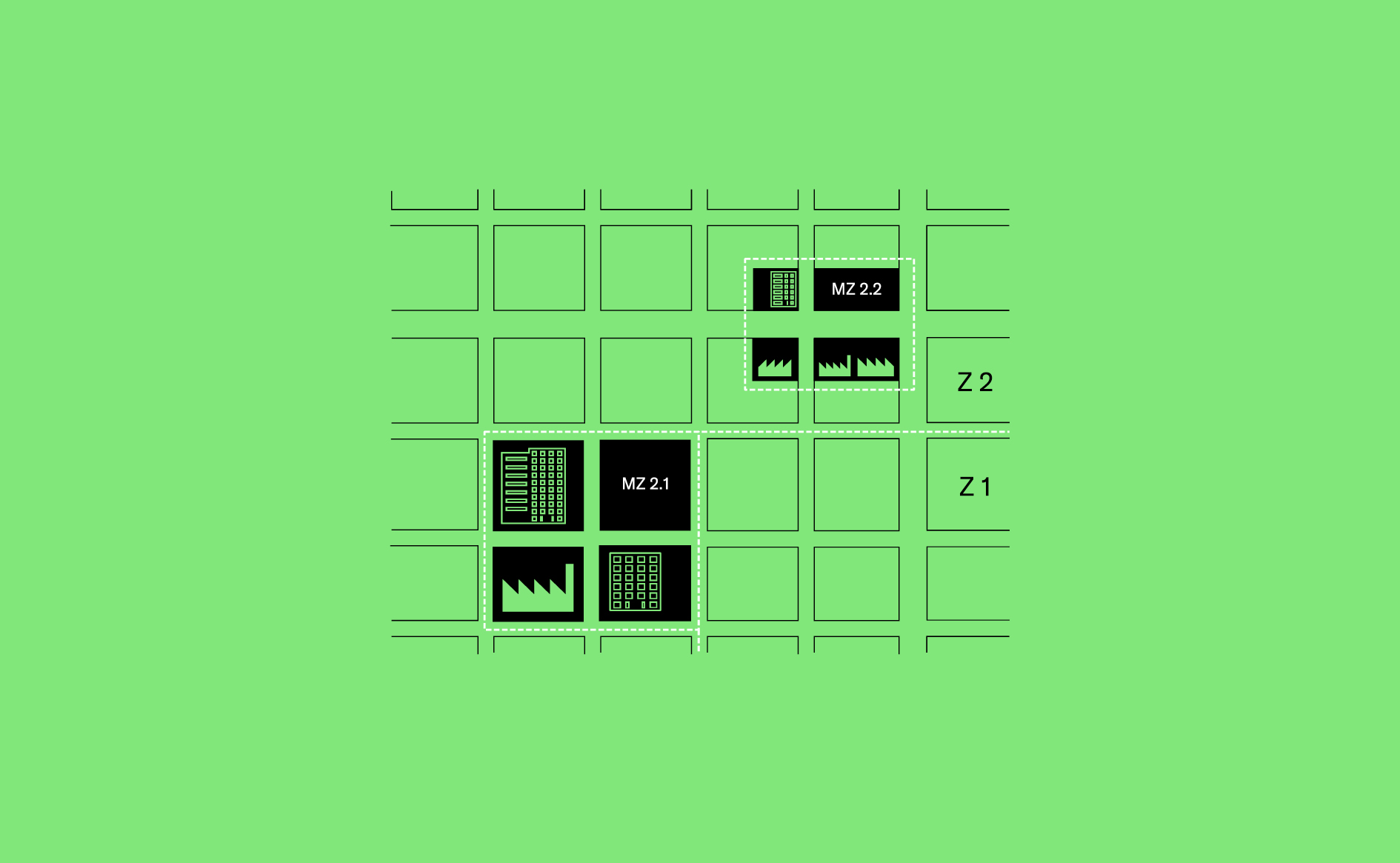
Strategically enabling zoning exceptions can protect vulnerable land uses or provide the grounds for experimentation in mixing land uses and building types.…
Read more
The environmental impact of manufacturing can impact areas far beyond the production site, requiring informed decisions by affected stakeholders to be made to avoid conflict and unintended consequences.
…
Read more
Public ownership of manufacturing space enables public interests to have an active stake in neighbourhood issues while ensuring space is available for unconventional or foundational forms of manufacturing.…
Read more
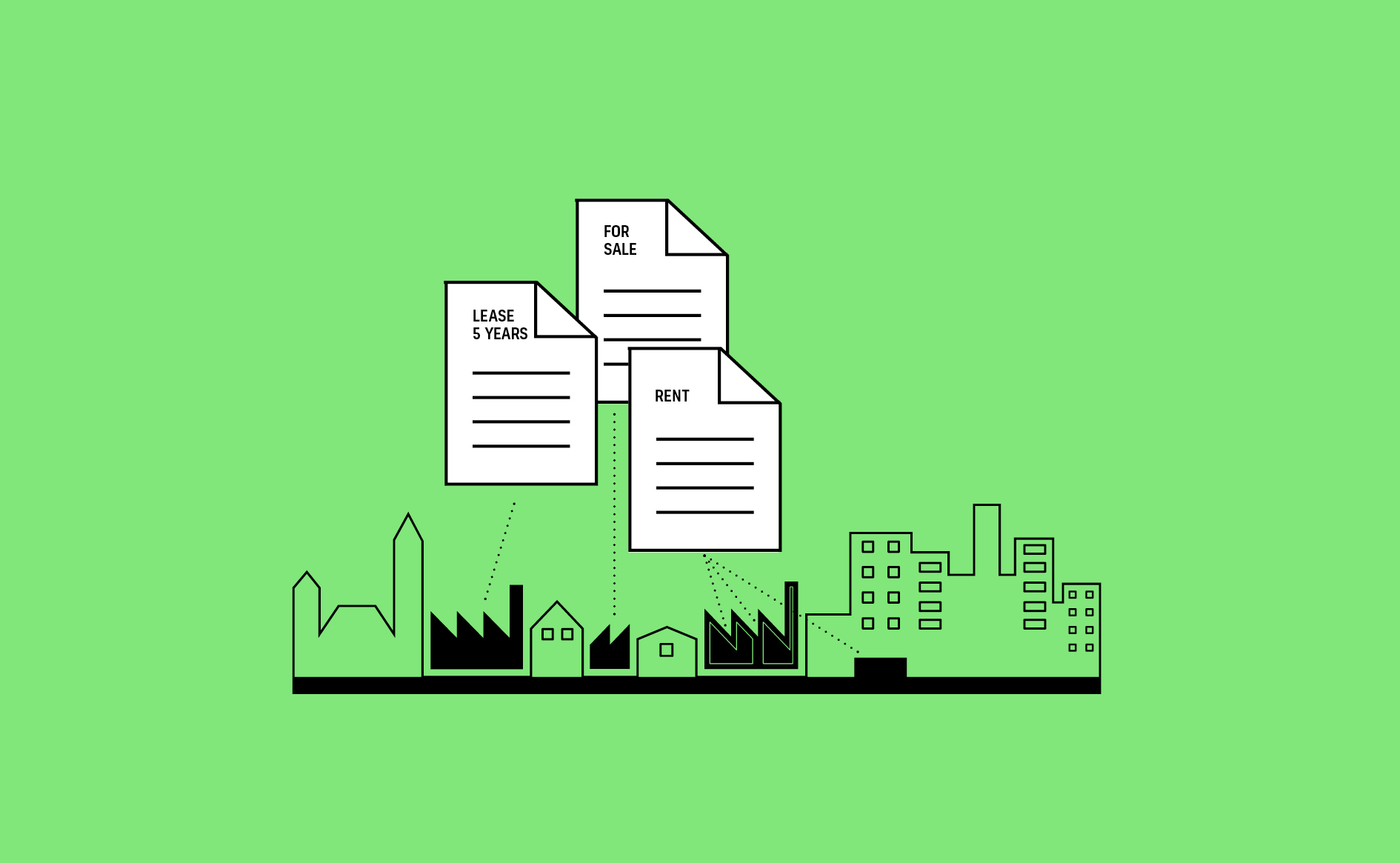

A range of land and property tenure models allows for manufacturing space to be accessible to businesses according to their financial means and ownership needs.…
Read more
Variations of unit sizes help to promote a variety of business types and facilitates manufacturers growing or shrinking without needing to leave an established neighbourhood.…
Read more

The location of a business will depend on defining strategic priorities regarding accessibility by clients, partners, staff and the cost of space.…
Read more
Manufacturing benefits from being near relevant infrastructure, multimodal logistics hubs and good access to distribution networks.
Read more
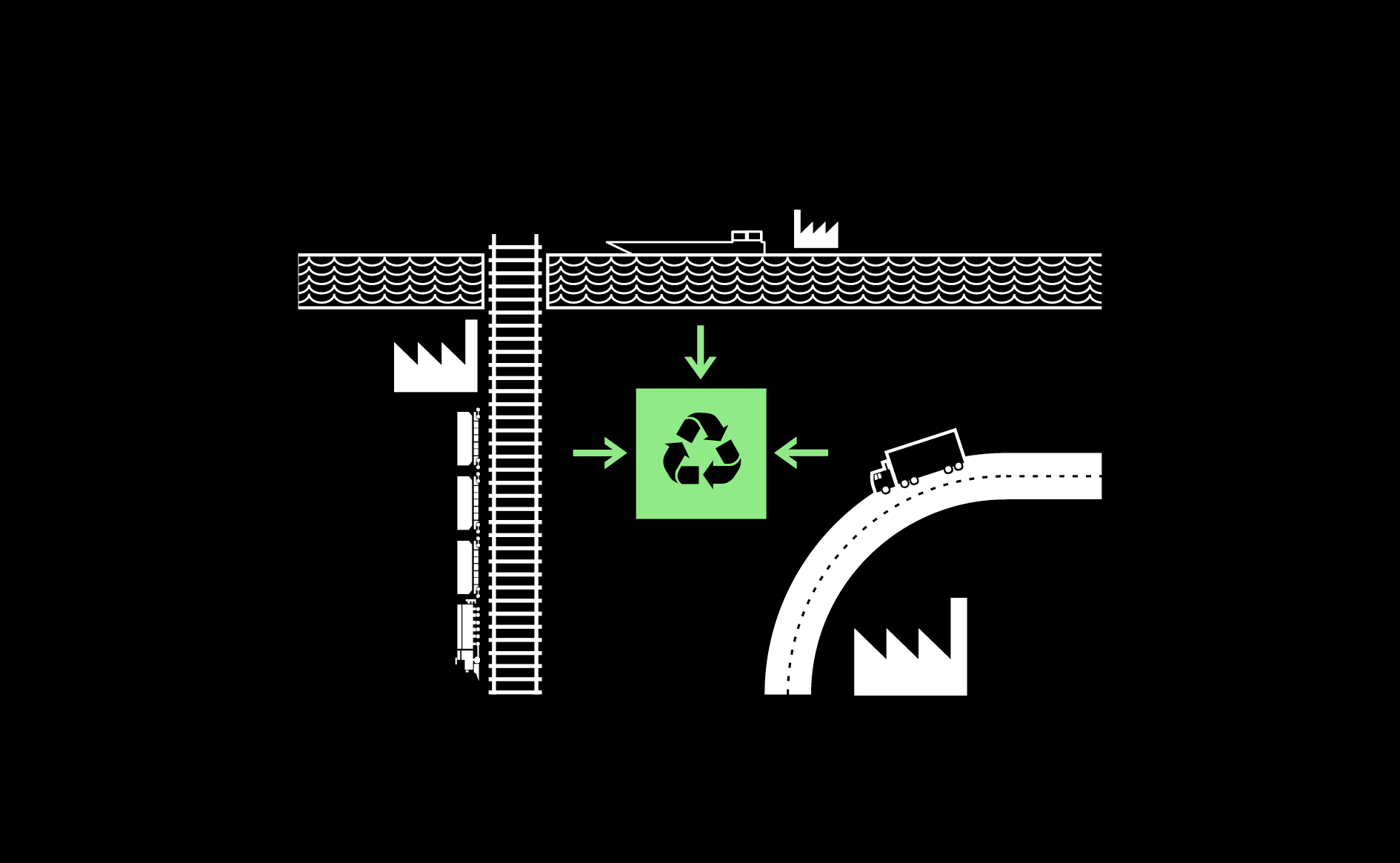
Waste processing and recycling facilities must be locally accessible through efficient logistics networks.
Read more
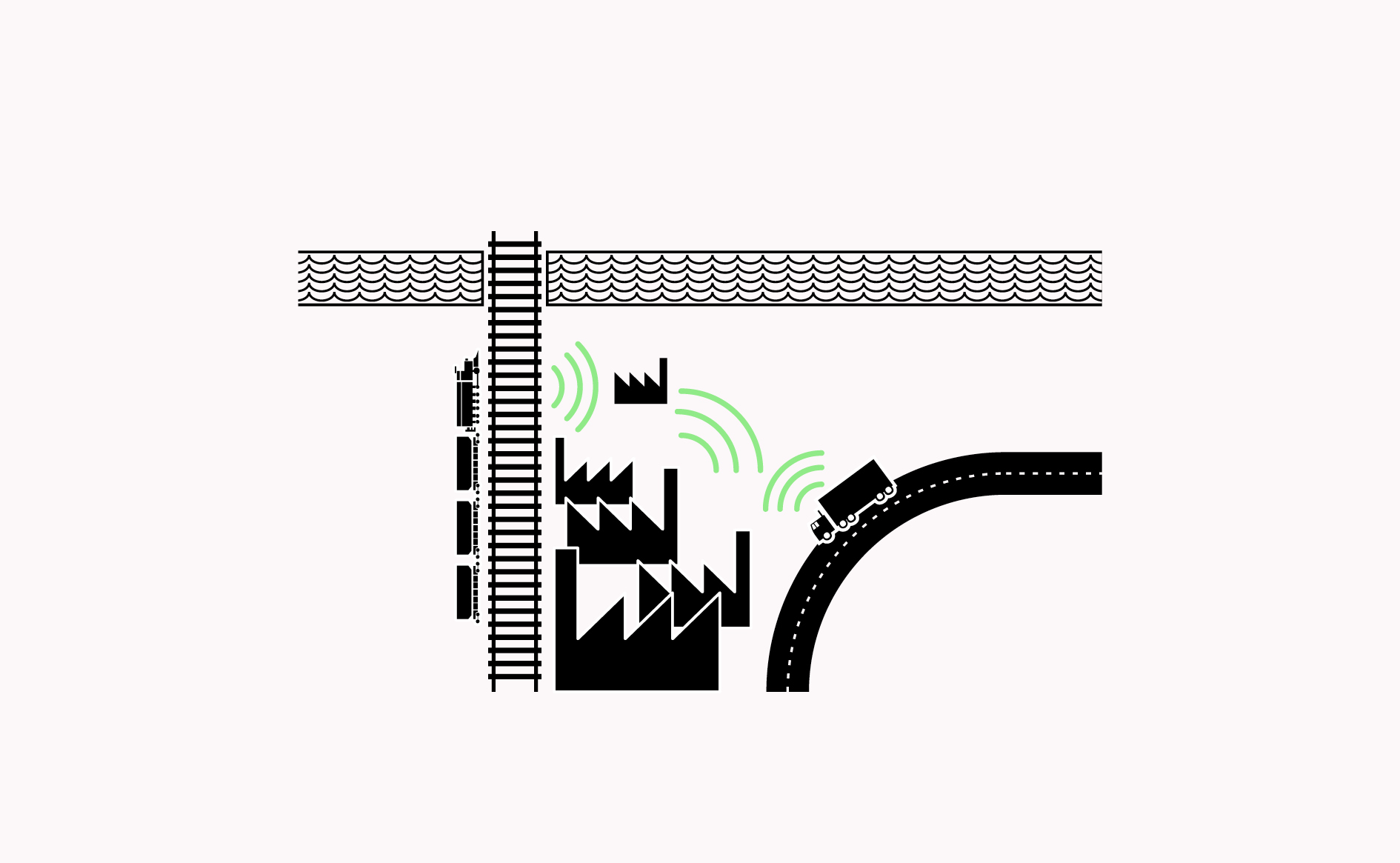
Concentrating manufacturing activities that produce noise, dust, and problematic odours along infrastructure, minimises nuisances.
Read more
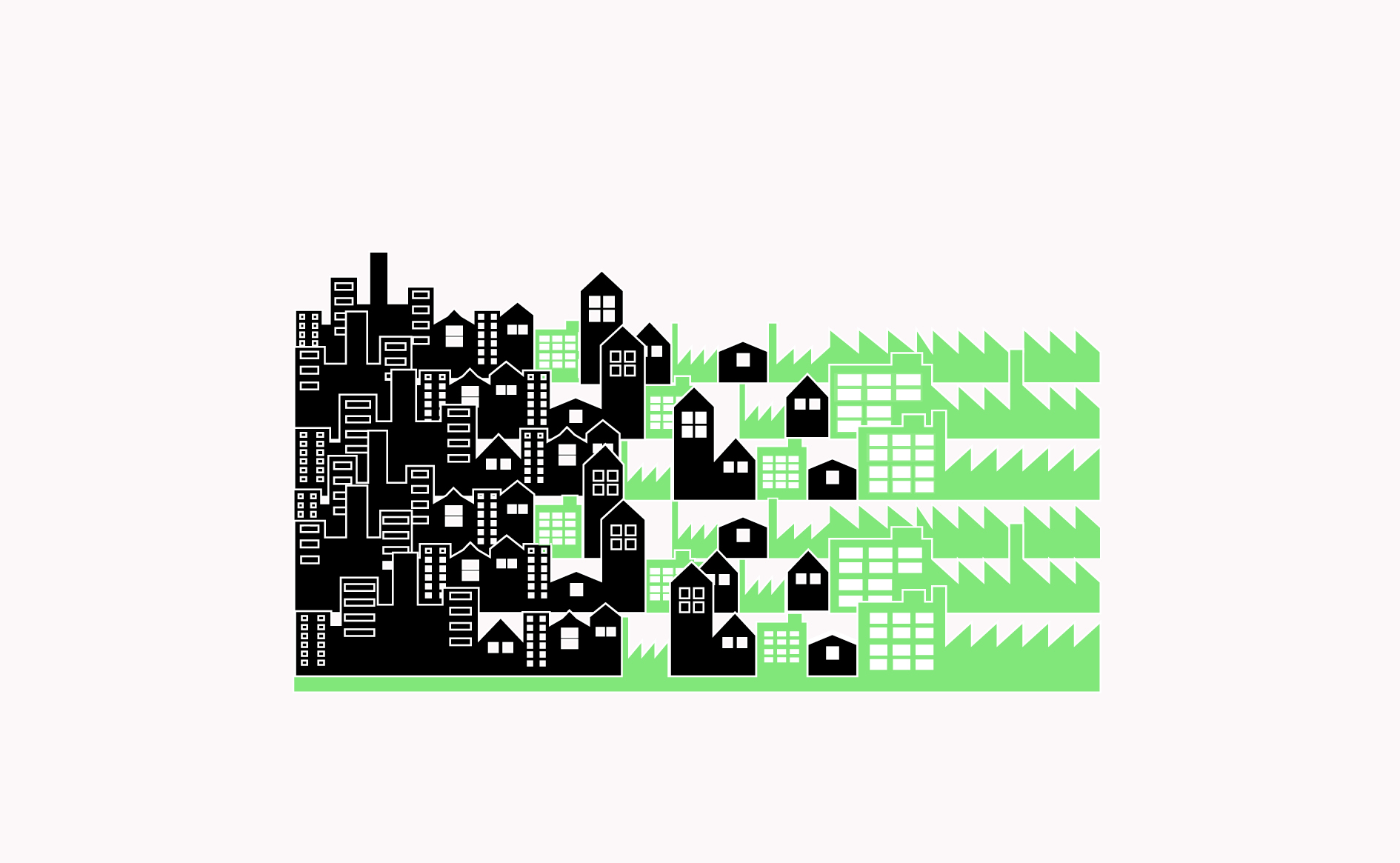
Zones adjoining industrial areas can provide ideal space for small to medium size manufacturing businesses and supporting services that help transition into mixed use and residential areas.…
Read more
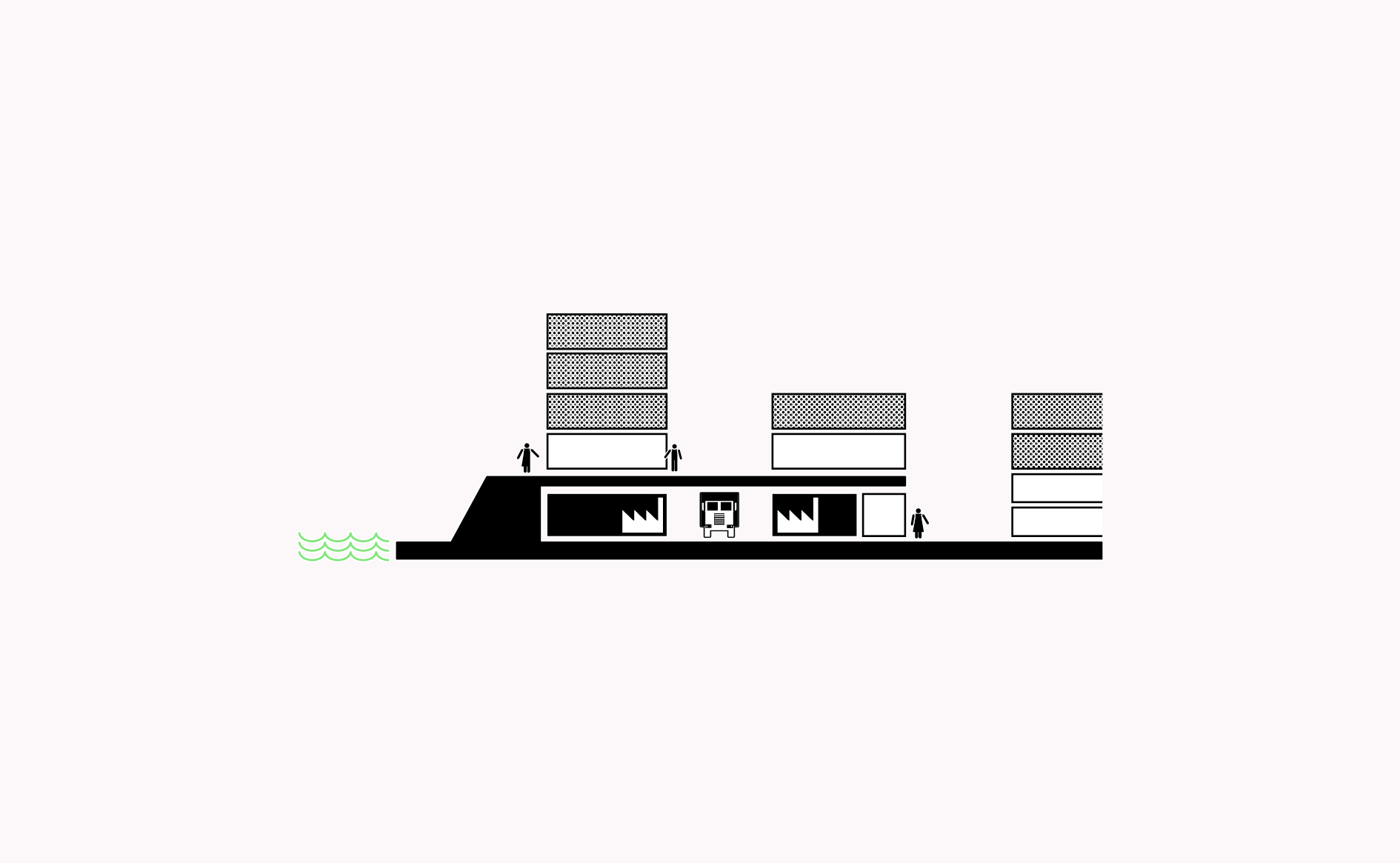
Making use of place qualities and particularly existing conditions along rivers, canals and railway arches can use these special conditions advantageously to accommodate manufacturing.…
Read more
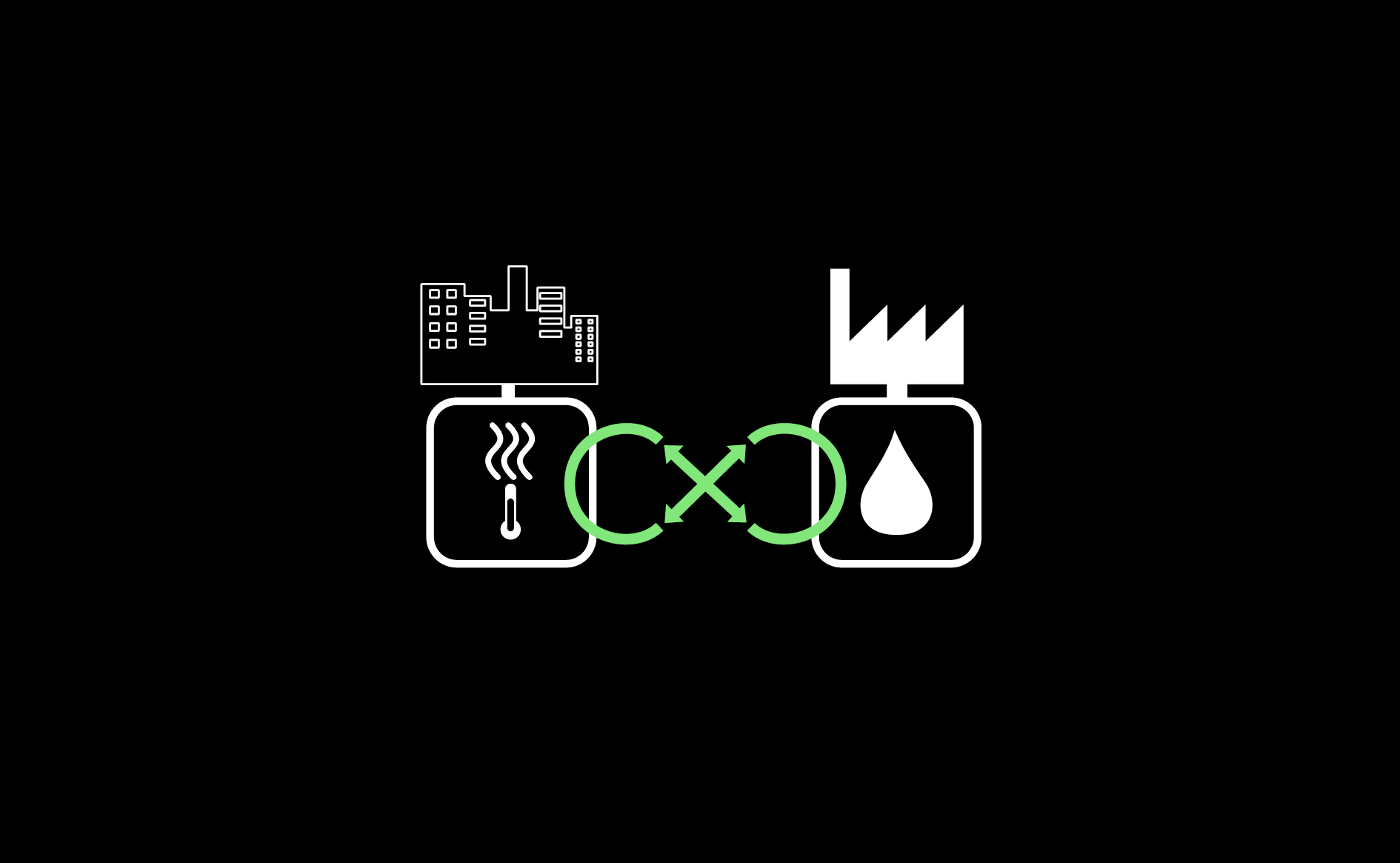
Local production of waste water, materials and heat could be turned into innovative new uses, to reduce the dependency on primary raw materials and reduce environmental pressures. …
Read more

Mixing complementary manufacturing with related activities creates conditions for efficient work flows and provides opportunities for resource and knowledge synergies through cross-sectoral innovation.…
Read more
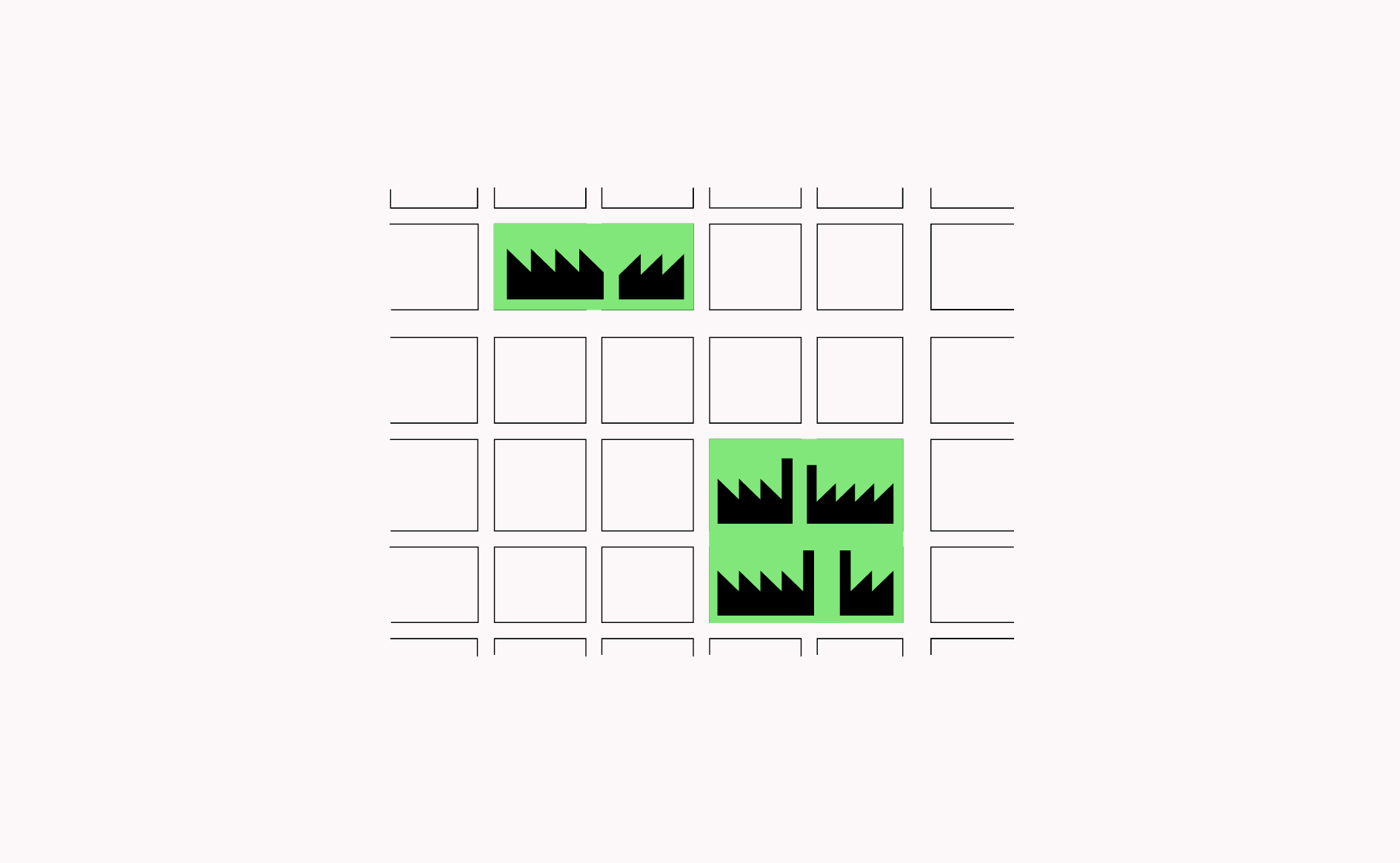
Clustering similar types of manufacturing promotes conditions for innovation, competition and collaboration while increasing access to staff and concentrating associated environmental issues. …
Read more
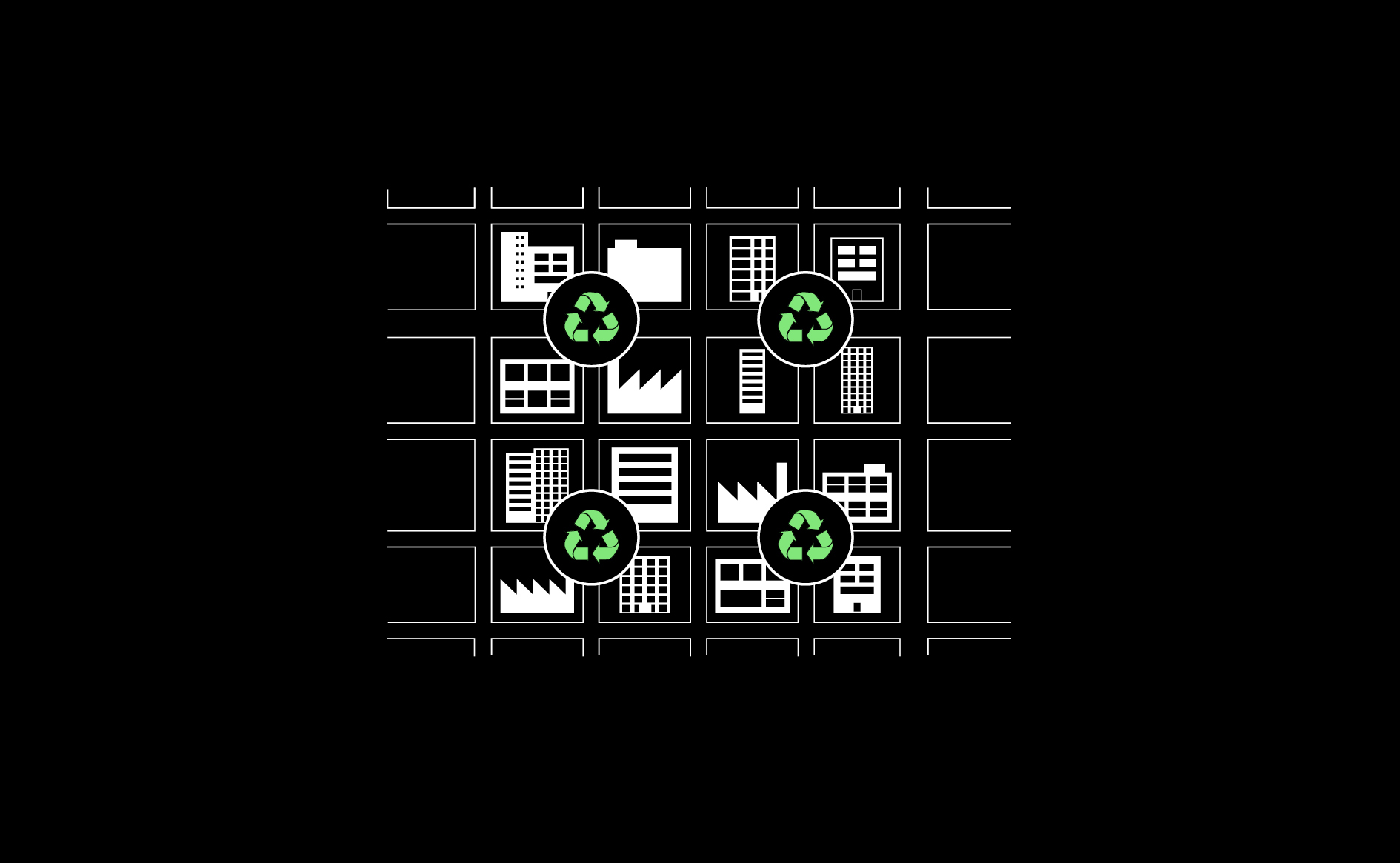
To ensure full recovery of waste streams, non-domestic waste collection points must be both easily accessible and well distributed across the city, into segregated waste streams to guarantee homogeneity, purity and maximise value and recovery potential. …
Read more
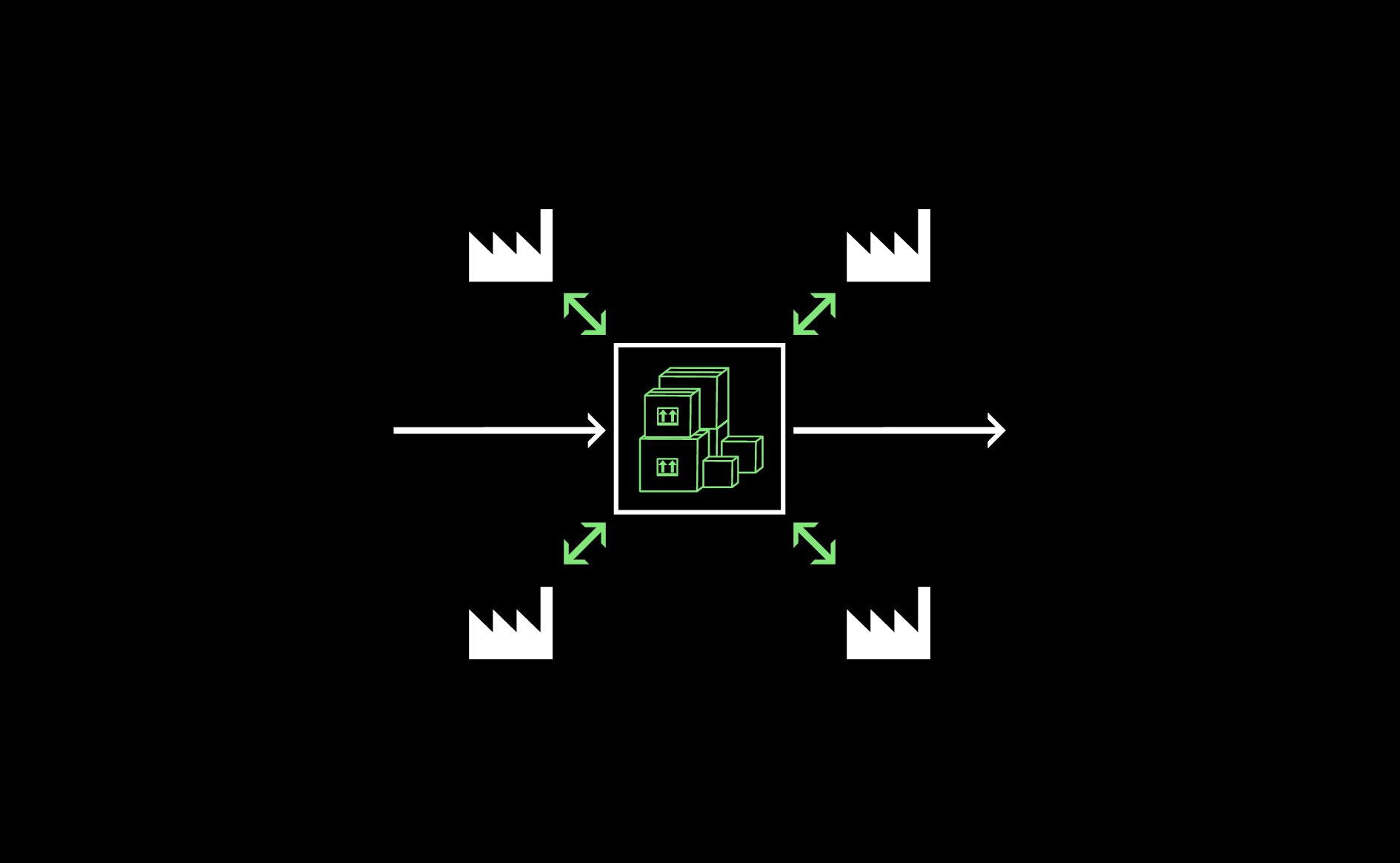
Central collective logistics space in accessible locations facilitates efficient delivery and discharge of goods while providing opportunities to store material or manufactured goods.…
Read more

Locating R&D testing facilities for manufacturing within knowledge hubs such as technology parks, innovation districts, and research centres promotes synergies in the use of technology and transfer of knowledge.…
Read more
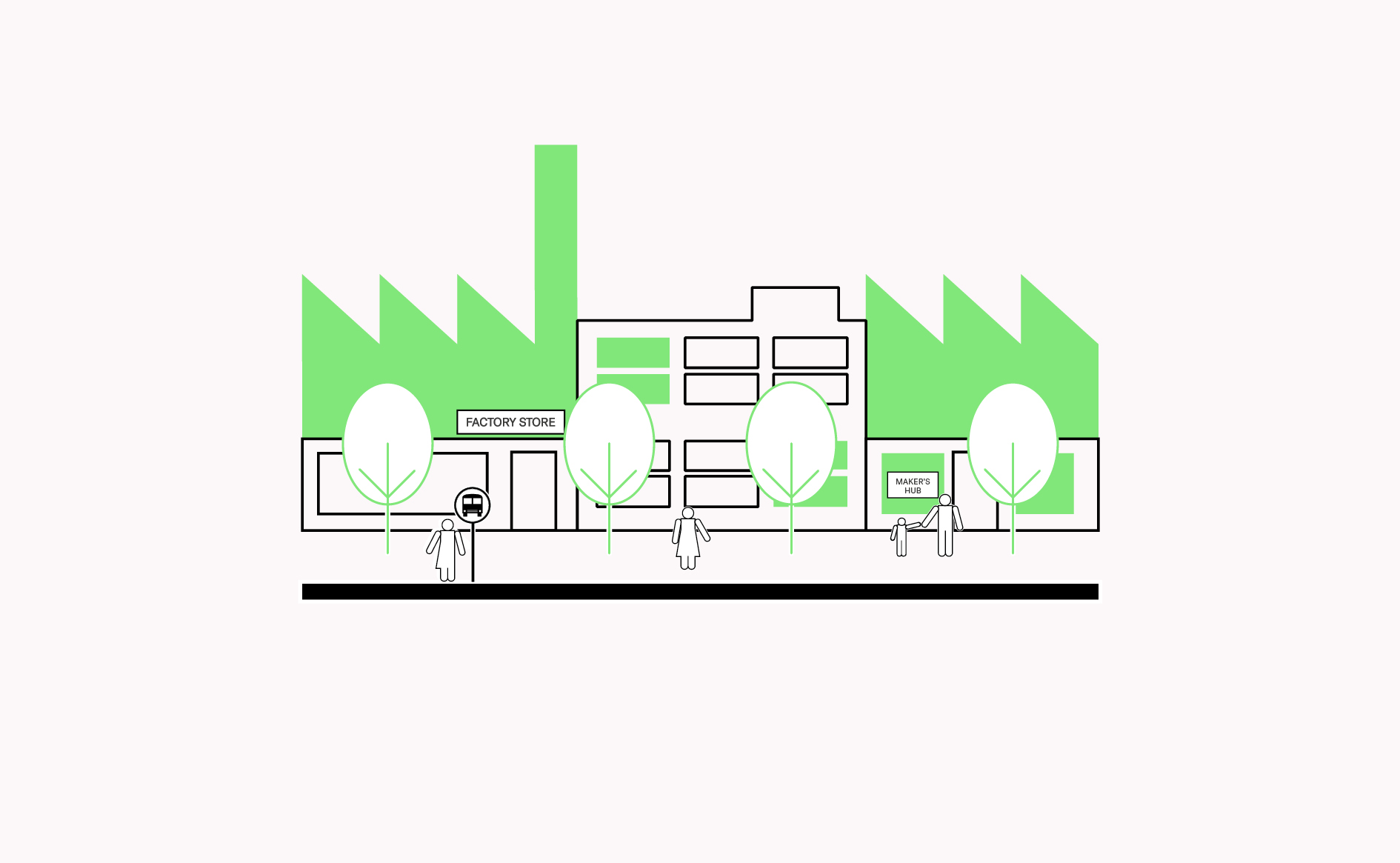
A high quality public realm is attractive for both employees and clients, increasing a sense of safety, encouraging mixed use, improving staff retention and encouraging visitors.…
Read more

Locating businesses according to similar environmental issues helps to minimise negative impacts of manufacturing by focusing on the block (noise and dust), streets (logistics) or neighbourhood (odours).…
Read more
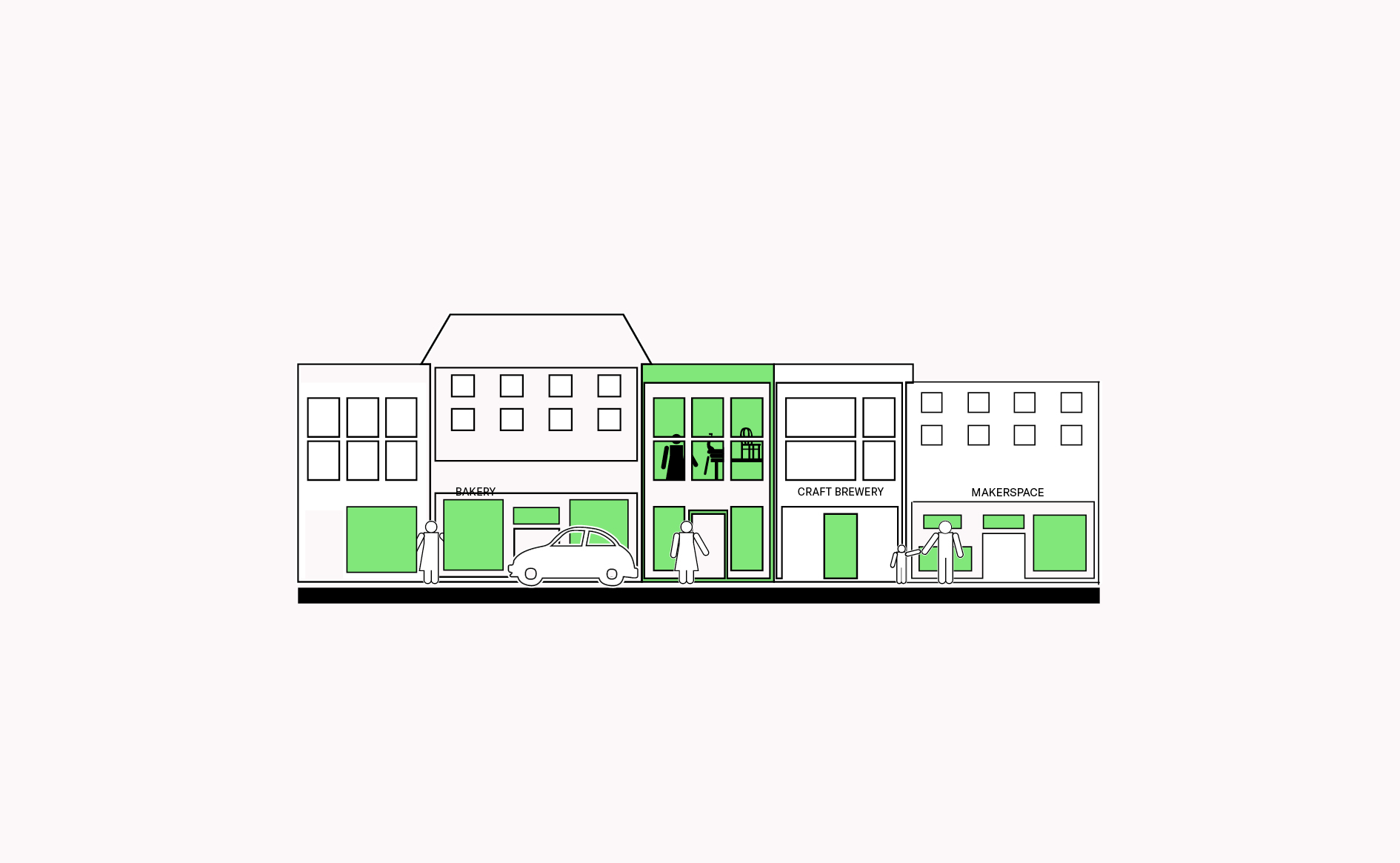
Concentrations of mixed use activities along high streets can take advantage of the best regional accessibility and the highest amount of pedestrian flows, enhancing visibility.…
Read more
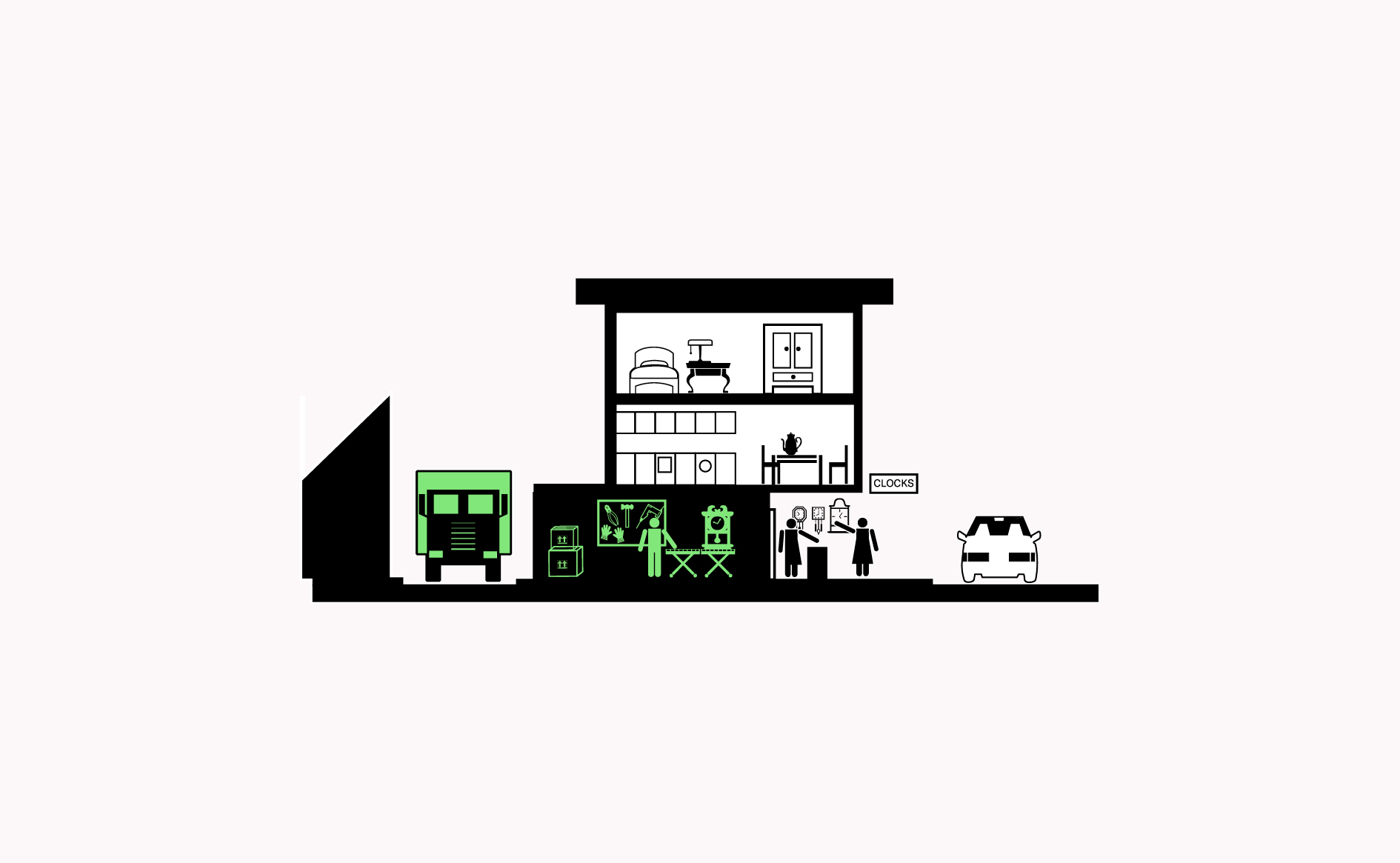
Locating manufacturing behind high streets, facilitates the movement of goods, provides flexible space for making, while located in proximity to complementary activities such as logistics, material suppliers and repair centres.…
Read more
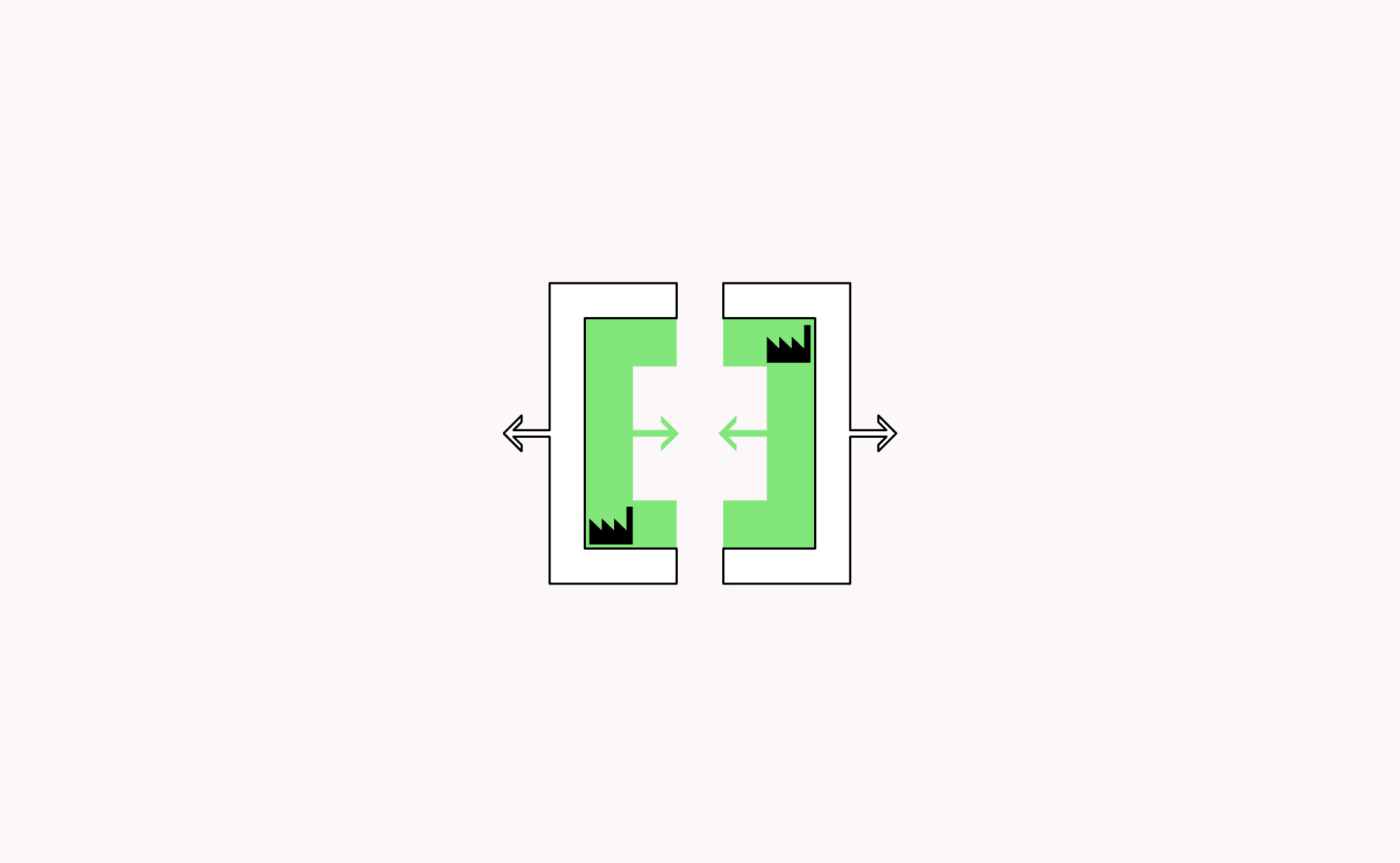
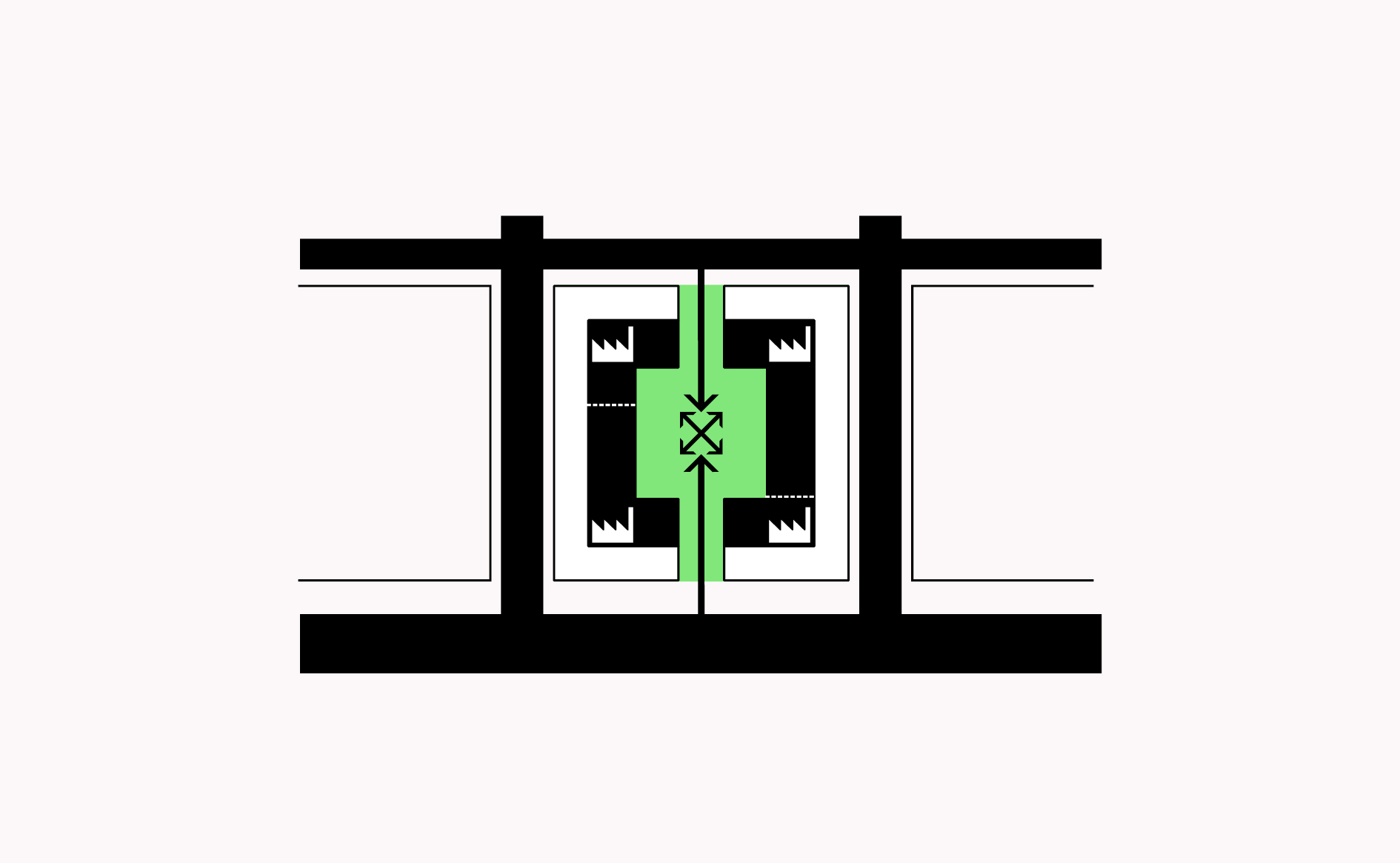
Organising manufacturing around courtyards inside blocks allows businesses to make noise, dust, move vehicles safely and provides additional space outside of the workshop area while allowing cohabitation with some forms of mixed use.…
Read more
Yards with sufficient space for turning and parking can facilitate safe loading and unloading, without disruption, in high density areas.
Read more
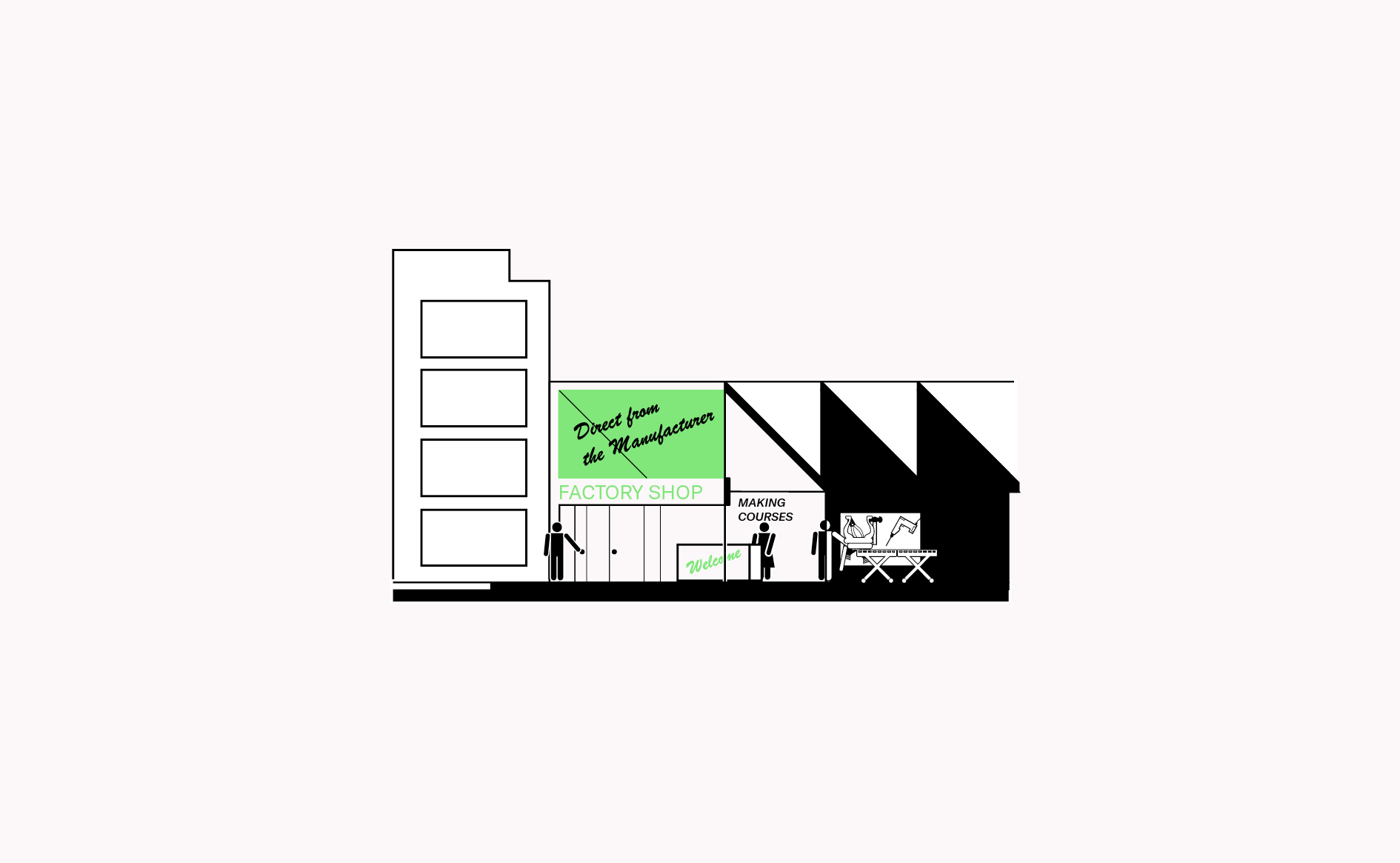
Activities which have a public interface achieve better neighbourhood integration and acceptance, while improving exposure to clients.
Read more
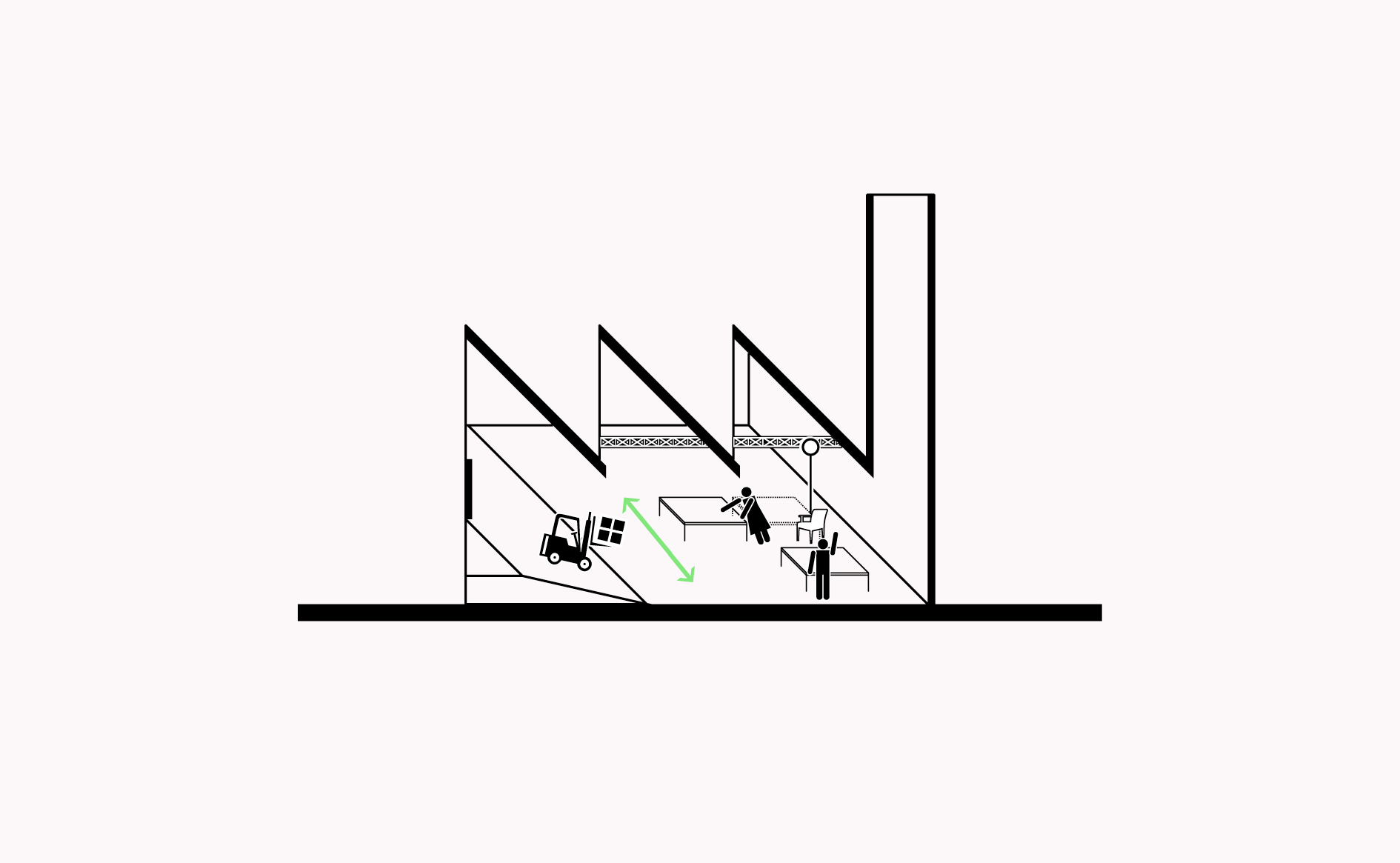
Horizontal organisation of manufacturing spaces, including smooth floors, overhead gantries and wide spacing between columns enables easy reconfiguration and safer working conditions.…
Read more
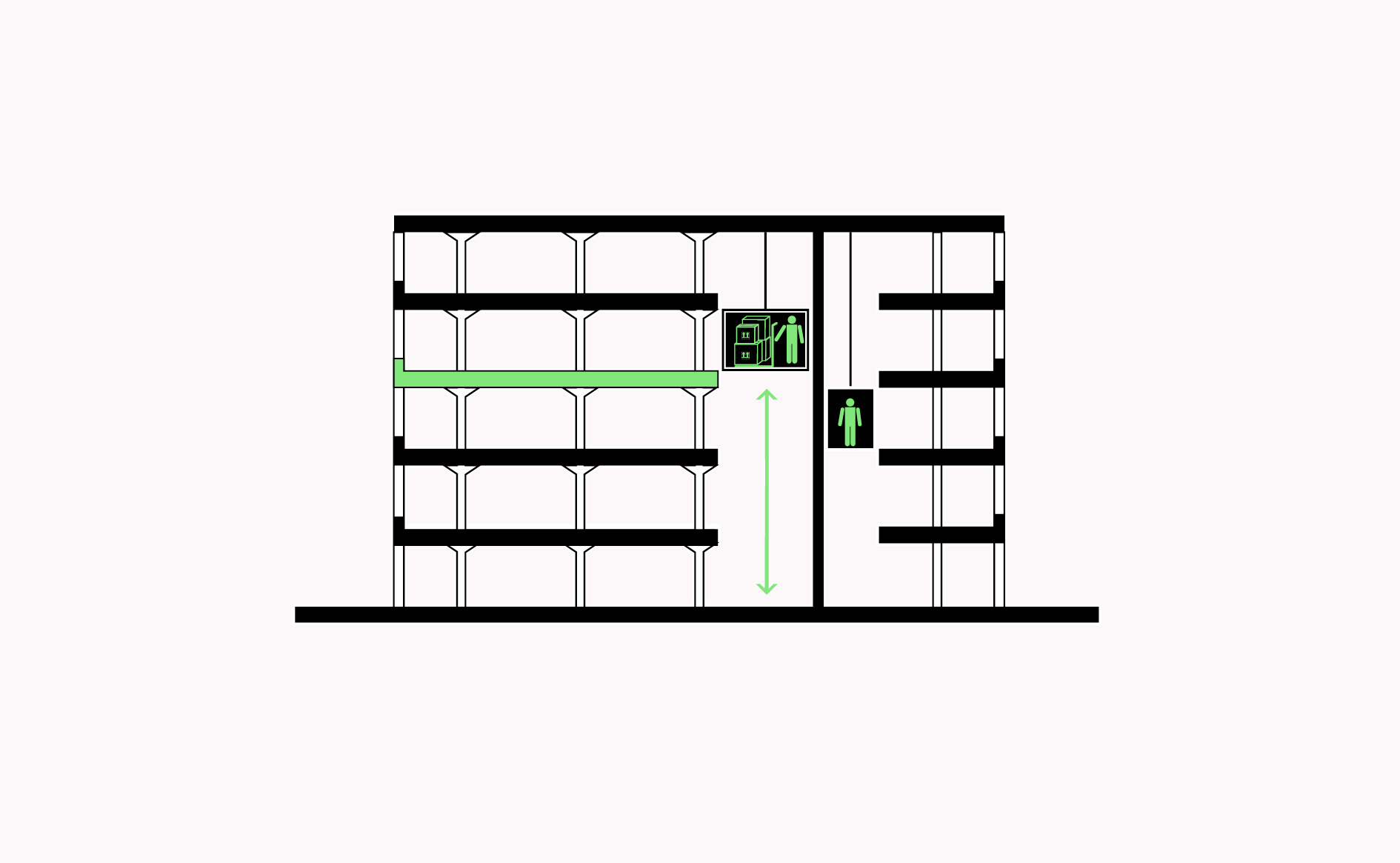
Goods lifts and heavy load-bearing floors in multi-storey buildings allow for industrial intensification and for buildings to adapt according to demand for space.…
Read more
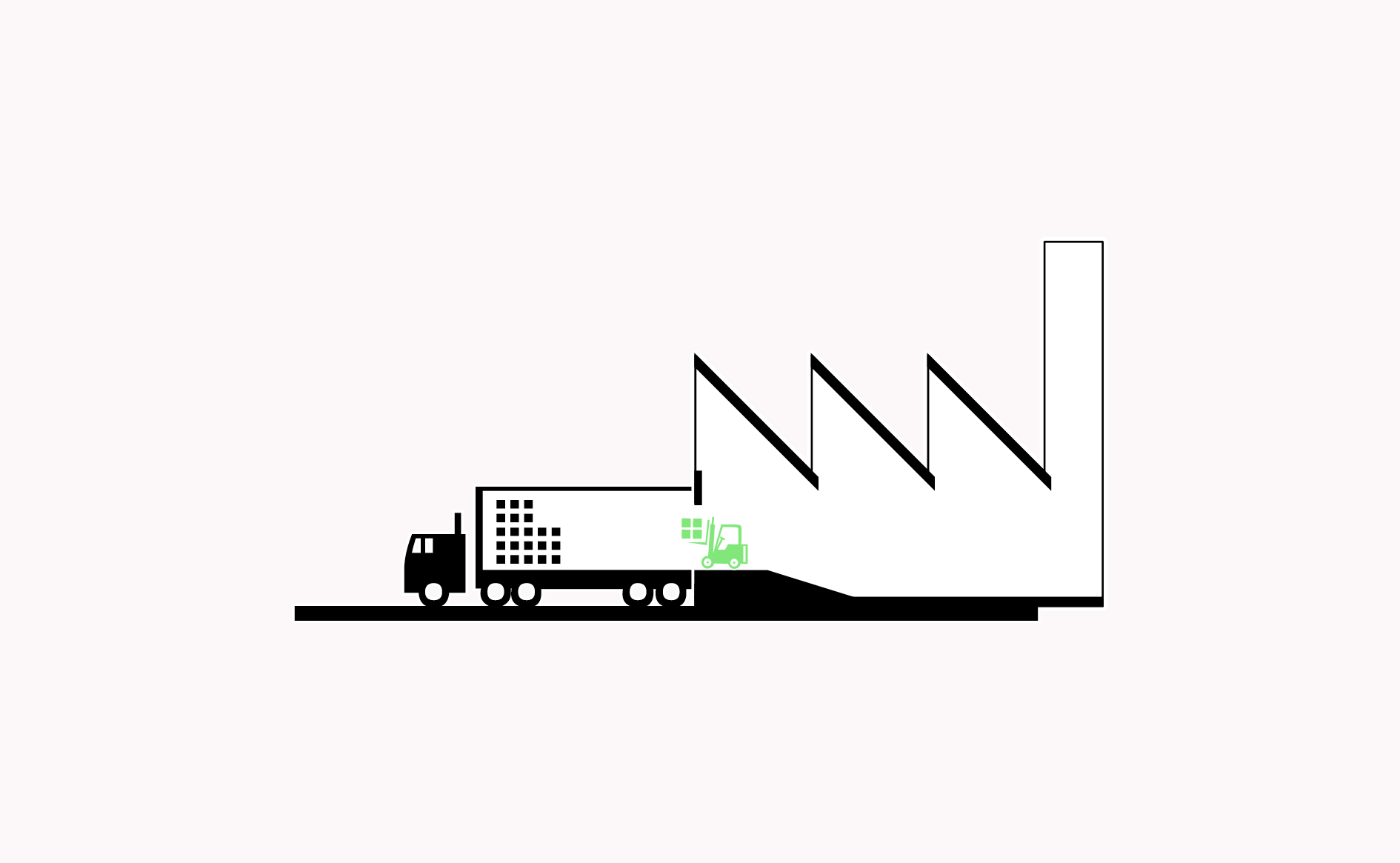
Loading docks, ramps and dedicated parking bays are essential to allow for a smooth transition of goods in and out of vehicles.…
Read more
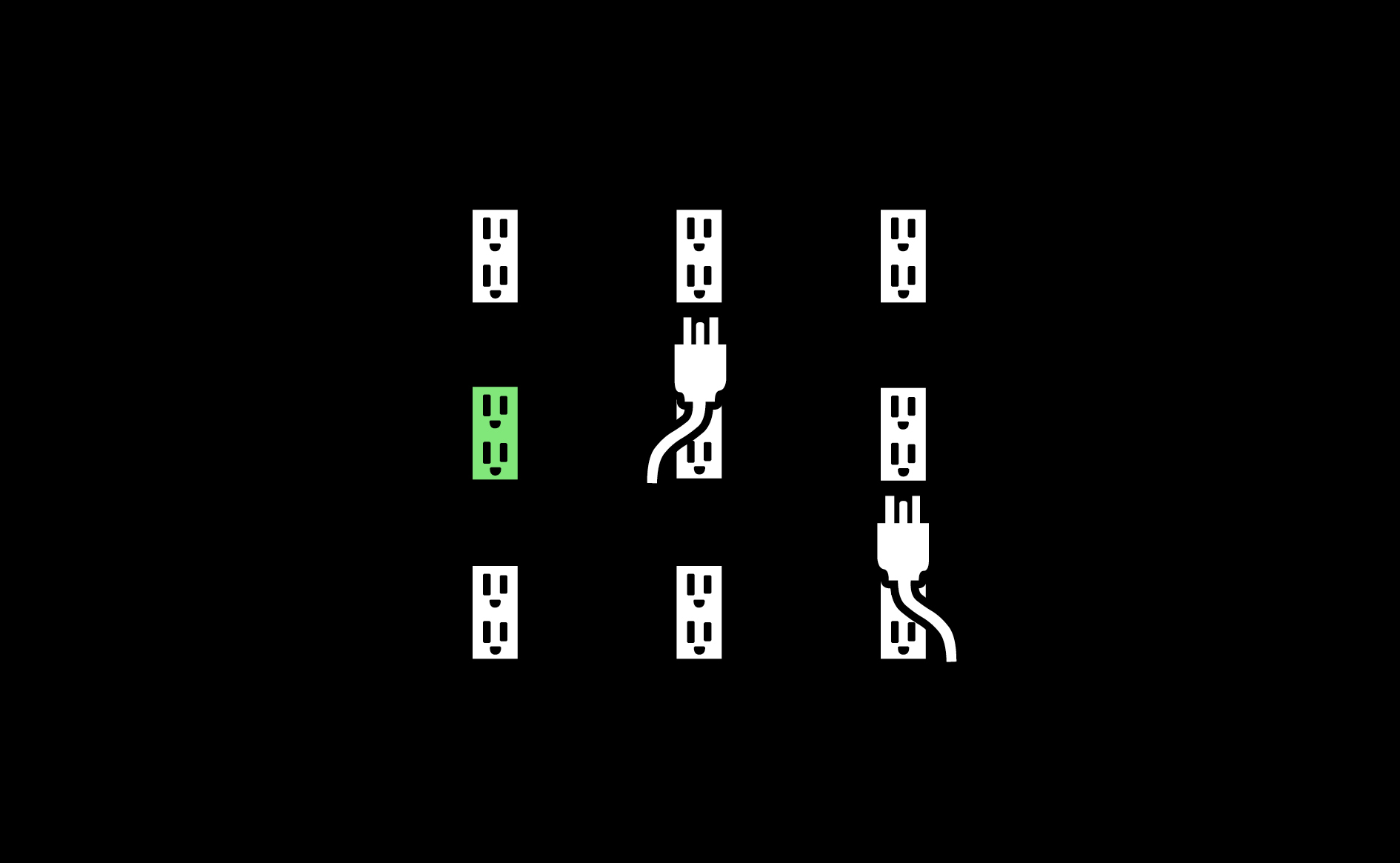
Well-distributed and adequate capacity of technical networks (electricity, water, ventilation, communications and distribution channels) allows for flexible, responsive and distributed manufacturing.…
Read more
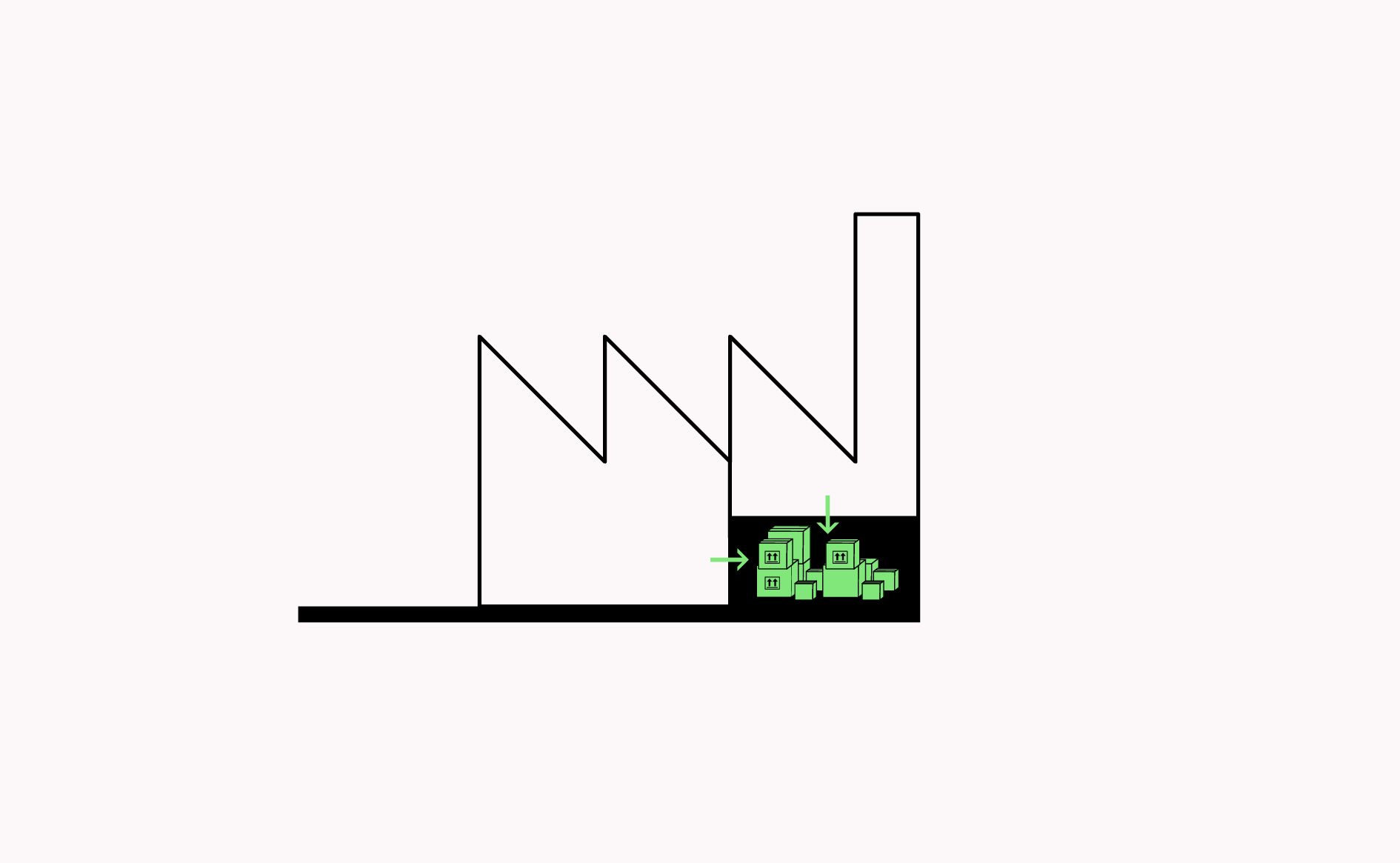
Manufacturing spaces with smart storage solutions allow for efficient use of space and production processes.
Read more
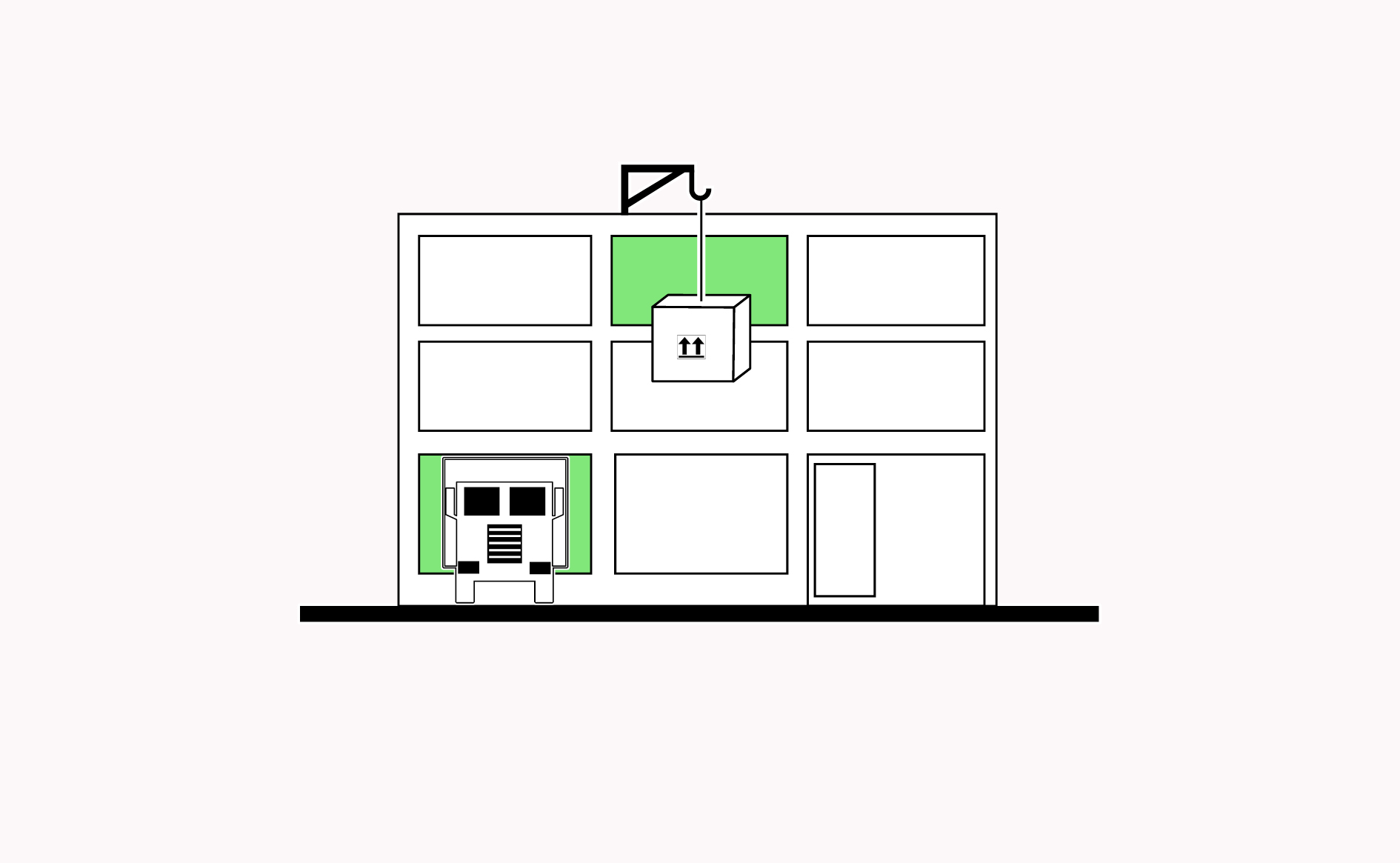
Large openings in buildings enable vertical and horizontal accessibility to access goods, materials and large equipment.
Read more

Roofs complement the performance of a building or intensifying land use, allowing for climate adaptation, food and energy production.
Read more
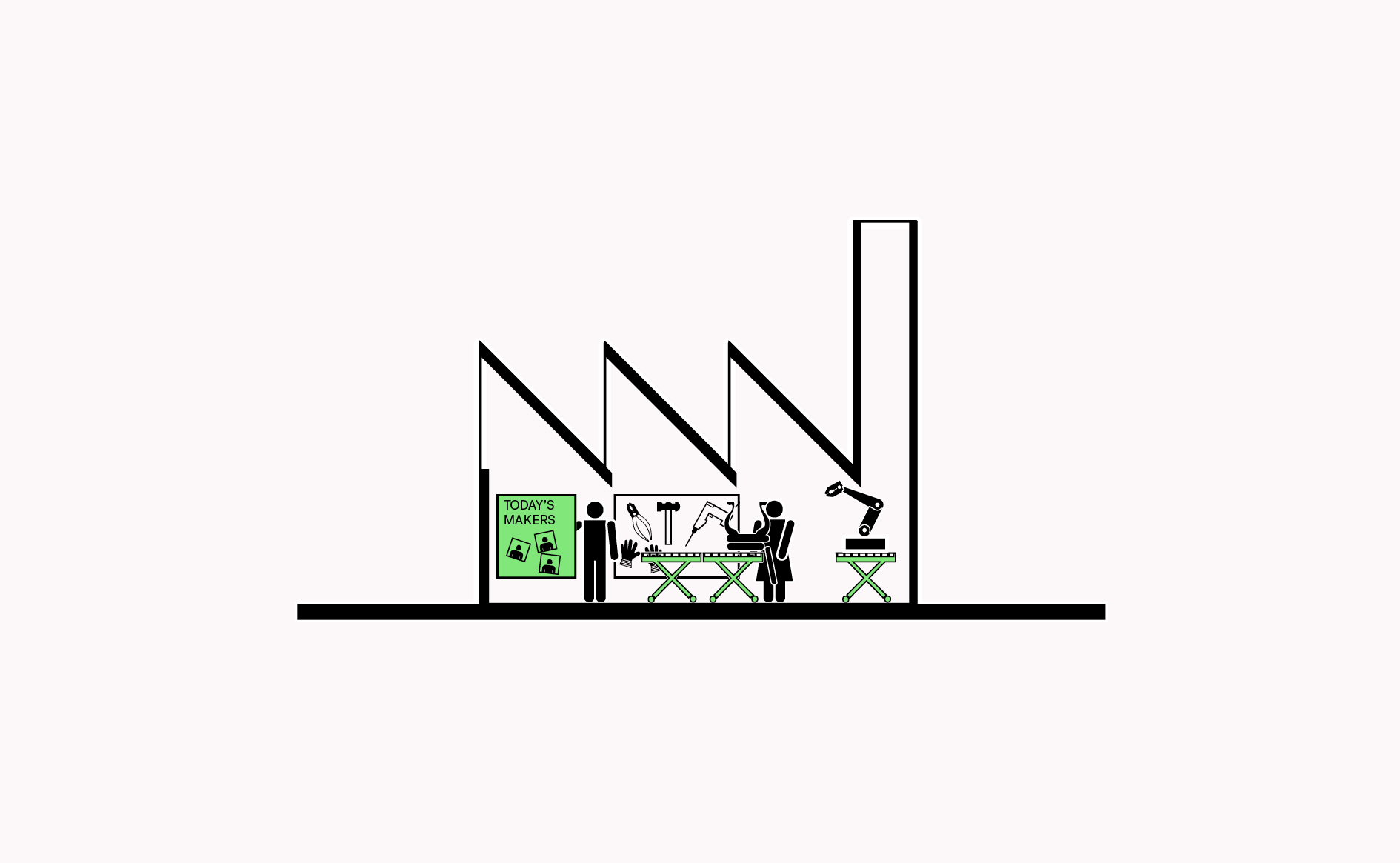
Smart use of space and technology through sharing can increase accessibility to expensive equipment, make more effective use of technology, while encouraging knowledge transfer between manufacturers.…
Read more
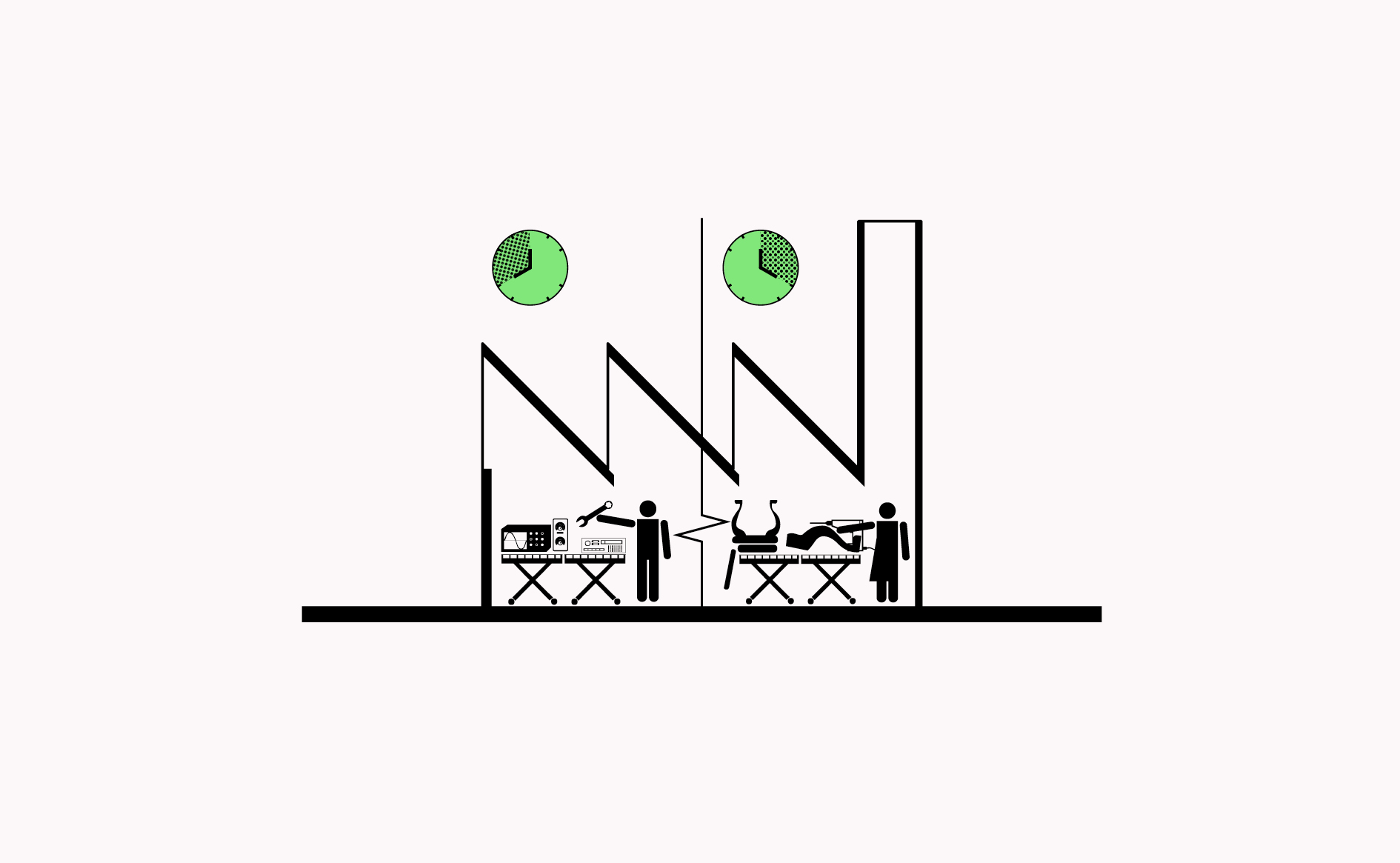
Meanwhile spaces can allow makers access to low-cost and low commitment access to space for making activities while also provide planners with a period to test new activities.
…
Read more

Meanwhile spaces can allow makers access to low-cost and low commitment access to space for making activities while also provide planners with a period to test new activities.…
Read more
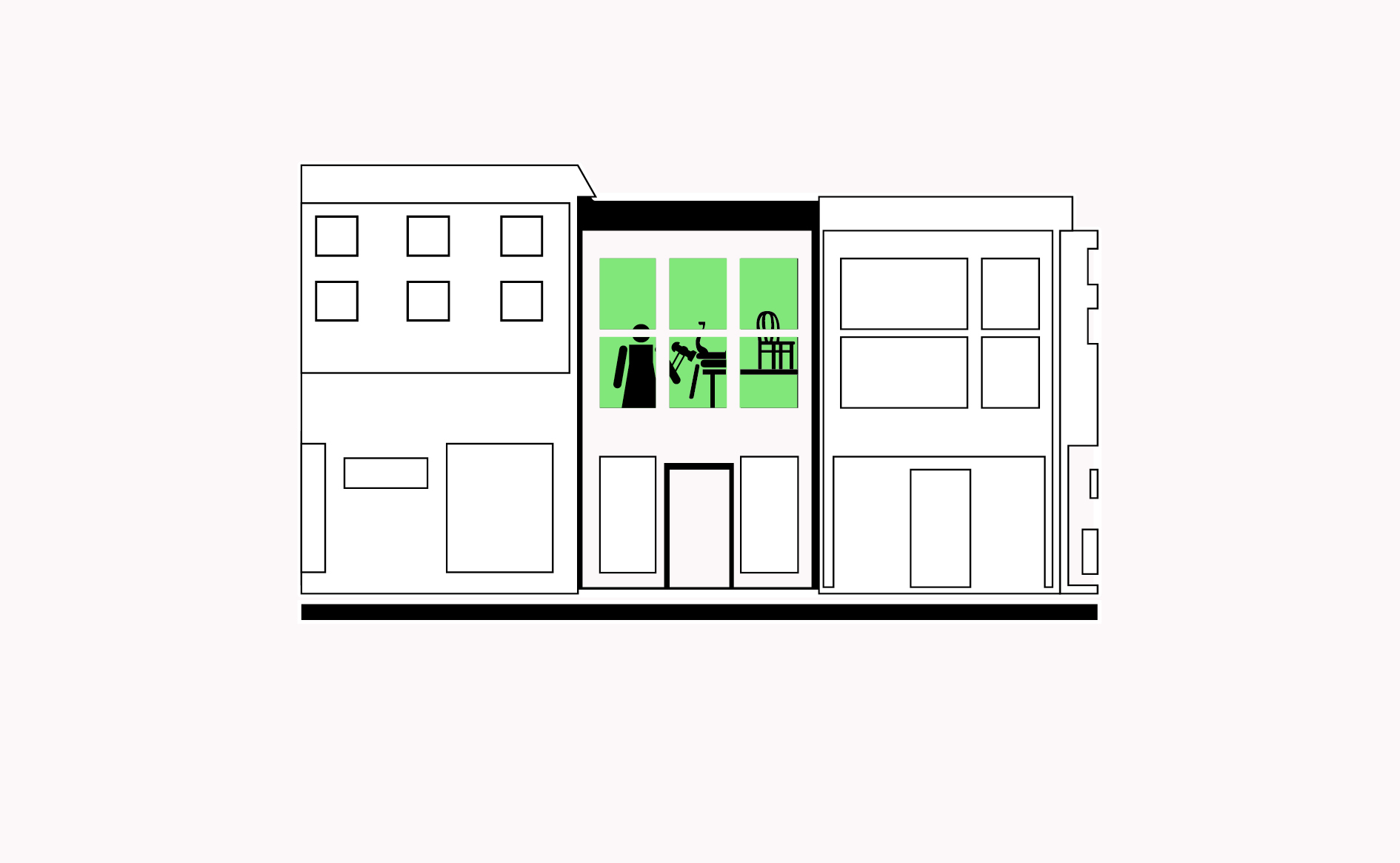

Homes can be a key part of local production processes and provide accessible and flexible income if domestic spaces and work-live concepts can be used for micro-manufacturing.…
Read more
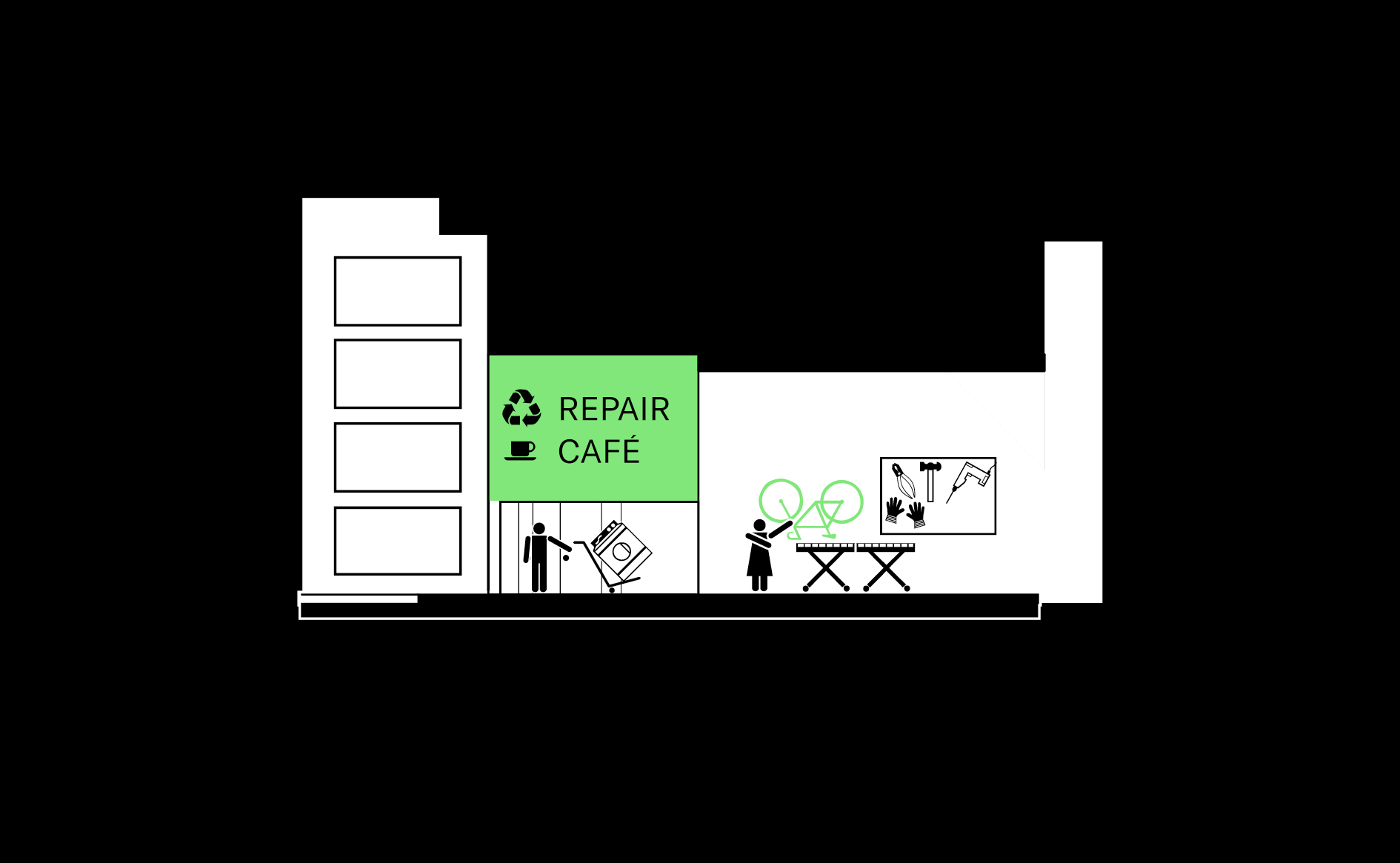
A network of local exchange and repair centres encourages re-use and re-circulation of consumer and professional goods, providing opportunities for local employment and community building.…
Read more

Training centres are necessary to facilitate education, share knowledge and develop relevant skills.
Read more
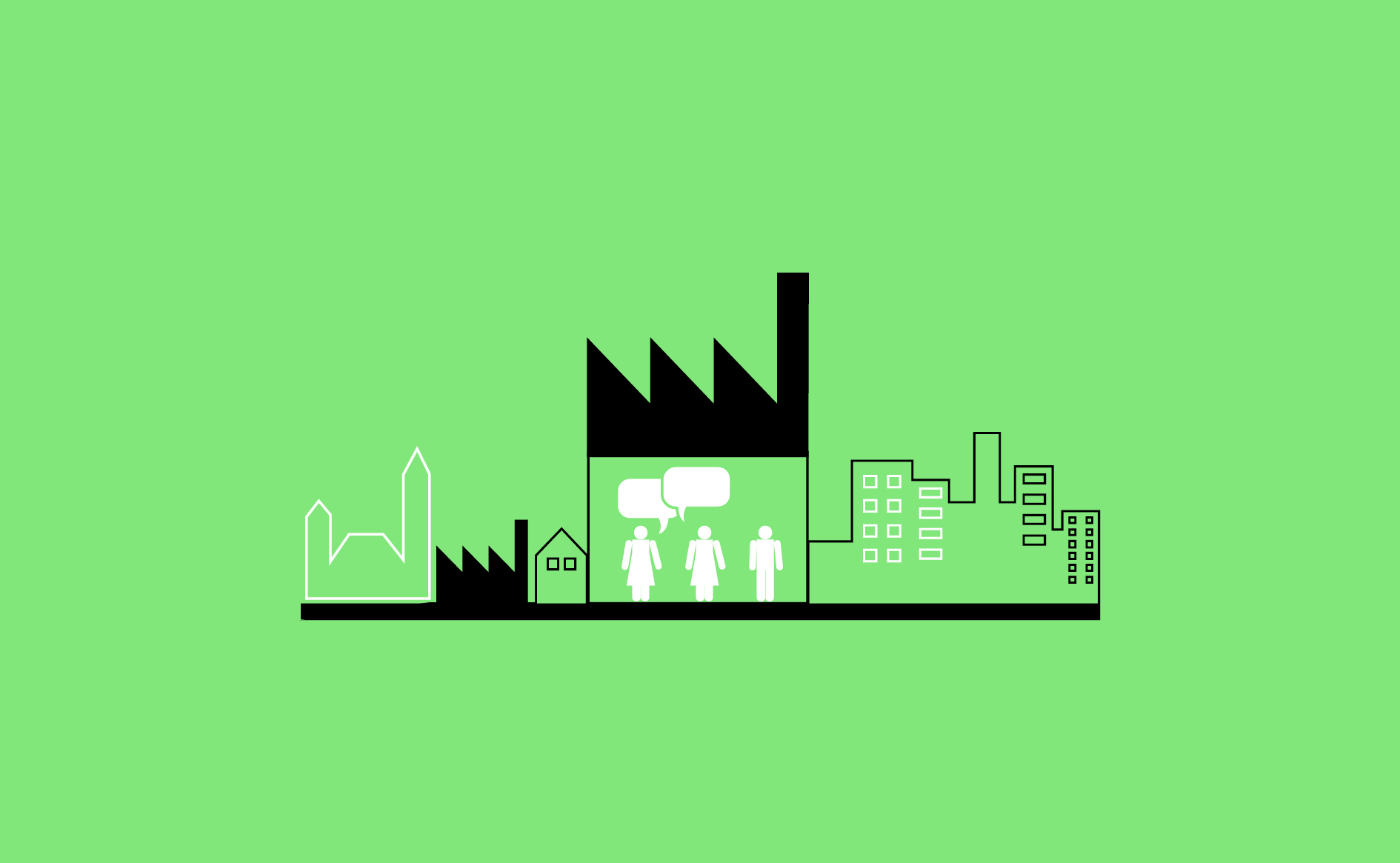
An inclusive hub helps facilitate knowledge exchange, nurture a place-based network of makers, encourage collaboration and provide businesses with a space to discuss collective problems and opportunities.…
Read more
















































